PAGE CONTENT:
Solid State Drives (SSDs) have revolutionized data storage, offering faster performance, greater durability, and improved energy efficiency compared to traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). As SSDs continue to become the standard for both personal and professional computing, understanding the common issues that can arise is crucial for maintaining their performance and longevity. This article will explore the reasons why SSDs may stop working and provide practical solutions to common problems.
Common Reasons Why SSDs Stop Working
● Physical Damage
One of the primary reasons SSDs fail is physical damage. Unlike HDDs, which have moving parts that are vulnerable to shock, SSDs are made of flash memory chips and are generally more resistant to physical impact. However, they are not entirely immune. Dropping the device or exposure to water can cause significant issues, leading to data loss or complete failure.
● Firmware Issues
Firmware plays a vital role in the performance of an SSD. Outdated or corrupted firmware can result in various problems, including reduced speed, failure to boot, or even complete unresponsiveness. Manufacturers regularly release firmware updates to address bugs, improve performance, and enhance security. Not updating your firmware can leave your SSD vulnerable to issues that might be resolved with a simple update.
● Connection Problems
Connection issues often manifest as the SSD not being detected by the system. Loose or damaged SATA cables, faulty connectors, or improper seating of the drive in the motherboard can lead to connectivity problems. This is particularly common in laptops or desktops that are moved frequently or have been opened for upgrades.
● Power Failures
Sudden power failures or surges can cause SSDs to malfunction. Unlike HDDs, which may have a more gradual shutdown process, an SSD may abruptly lose power during read or write operations, leading to data corruption or loss. Always ensure that your system is connected to a reliable power source or invest in an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to mitigate this risk.
● File System Corruption
File system corruption can happen due to improper shutdowns, malware attacks, or even software glitches. When the file system is corrupted, the SSD may become unresponsive, preventing access to stored data. Although this problem can be annoying, it is frequently resolvable with the correct resources and methods.
● Wear Leveling and Endurance Limitations
Every SSD has a limited lifespan, measured in terabytes written (TBW). Over time, the process of writing and erasing data wears out the memory cells. SSDs use wear leveling algorithms to distribute write and erase cycles evenly across the memory cells. However, if an SSD reaches its endurance limit, it may stop working. Regular monitoring of the SSD’s health can help prevent issues related to wear and tear.
Diagnosing SSD Problems
● Checking SSD Health
Before attempting any fixes, it's essential to assess the health of your SSD. Various software tools can help you monitor the status of your SSD. For example, CrystalDiskInfo provides a detailed overview of the drive's health, including temperature, wear leveling count, and other SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) attributes. Manufacturer-specific tools, like Samsung Magician for Samsung SSDs or Crucial Storage Executive for Crucial SSDs, offer additional features, such as firmware updates and performance benchmarks.
● Running Diagnostic Tests
Running diagnostic tests can help identify issues with your SSD. Many SSD manufacturers provide diagnostic tools that can check for errors, measure performance, and even perform firmware updates. Using these tools can give you a better understanding of your SSD's condition and whether any repairs are necessary.
Common SSD Issues and How to Fix Them
● SSD Not Detected by the System
If your SSD is not detected by your computer, follow these steps:
- Check Connections: Ensure that the SSD is correctly connected to the motherboard and that all cables are secure. If necessary, unplug and replug the connections.
- Try a Different SATA Port: If the SSD is still not detected, connect it to a different SATA port on the motherboard. Sometimes, the issue may lie with the port itself.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that your SATA controller drivers are up to date. Go to the manufacturer's website for the latest drivers.
- BIOS Settings: Enter your computer's BIOS settings to see if the SSD is recognized. If not, check if the SATA mode is set correctly (AHCI is recommended for SSDs).
- Test on Another Computer: If possible, connect the SSD to another computer to determine if the issue is with the SSD itself or the original system.
● Slow Performance
If your SSD is running slower than expected, consider the following fixes:
- Enable TRIM: TRIM helps the SSD manage unused data more effectively, enhancing performance. To enable TRIM on Windows, open Command Prompt as an administrator and type:
fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify 0
- Check Background Processes: High CPU usage due to background applications can slow down SSD performance. Use Task Manager to identify and close resource-intensive programs.
- Firmware Update: Check for firmware updates for your SSD. Visit the manufacturer's website for instructions on how to update your firmware.
- Free Up Space: SSDs perform better when they are not completely full. Aim to keep at least 10-20% of the SSD's capacity free.
- Disk Cleanup: Utilize Windows' built-in disk cleanup tool to clear out extraneous files and make space.
● Read/Write Errors
Read/write errors can occur for various reasons. Here's how to address them:
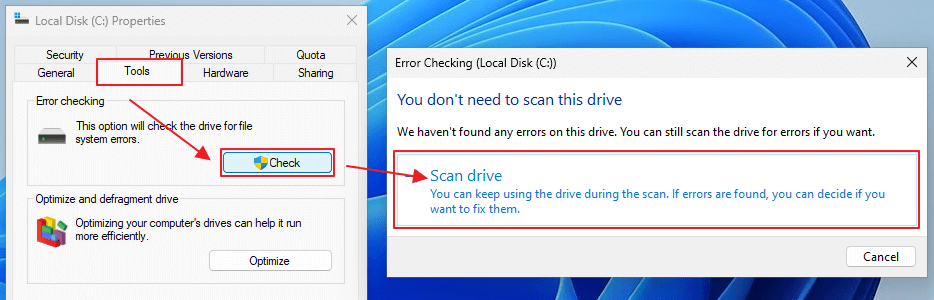
- Run Error Checking: Use Windows Error Checking utility to scan and fix file system errors. In File Explorer, right-click the SSD, choose Properties, navigate to the Tools tab, and then click "Check."
![Run Error Checking]()
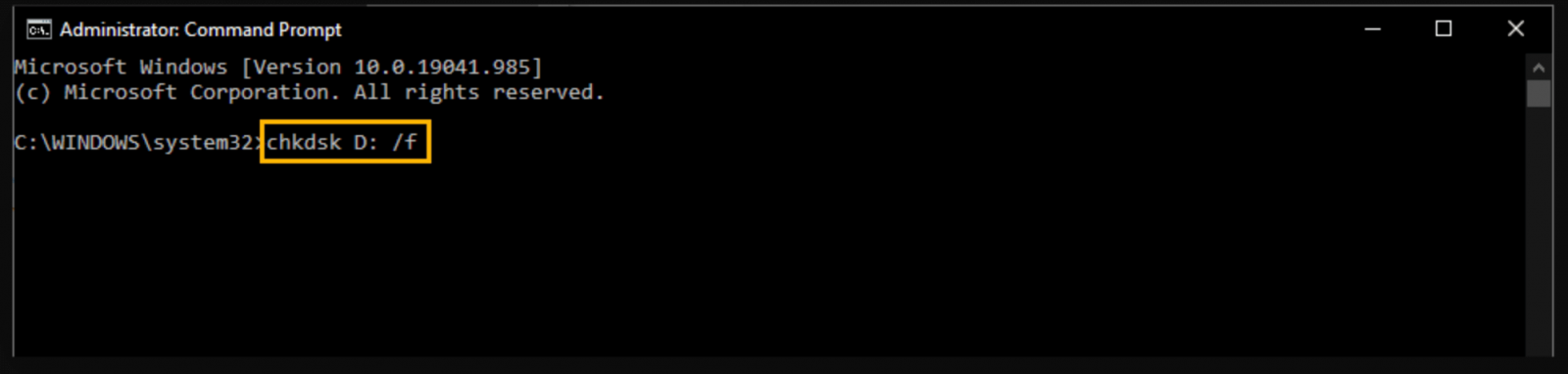
- 2.Use Disk Repair Tools: File system problems can be fixed with the aid of programs like CHKDSK. As an administrator, launch Command Prompt and enter:
chkdsk X: /f
![Use Disk Repair Tools]()
(Replace “X” with the drive letter of your SSD.)
- Check for Malware: Malware can cause read/write errors. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to ensure your system is clean.
- Check SSD Health: Utilize SSD health monitoring tools, such as CrystalDiskInfo or the manufacturer's diagnostic software, to check for any signs of impending failure. Look for warning signs such as high temperatures, increased wear leveling counts, or errors reported in the SMART data. If the SSD shows signs of significant deterioration, consider replacing it.
- Backup Your Data: If you start experiencing frequent read/write errors, back up your data immediately. Use reliable backup software or disk cloning software to ensure your important files are secure. If the SSD continues to fail, having a backup will prevent data loss.
- Secure Erase: If you cannot resolve read/write errors through conventional means and the SSD is still under warranty, consider performing a secure erase. This process restores the SSD to its factory state and can help fix issues caused by data corruption. Make sure you have a backup before continuing, though, as this will remove all data on the drive.

How to Securely Erase SSD
Securely erase SSD with built-in tools or third-party data erasure software, 100% safe, no physical damage.
● SSD is Full
An SSD that is completely full can lead to performance issues and errors. To address this:
- Delete Unnecessary Files: Go through your files and delete those that are no longer needed. Focus on large files, such as videos, installers, and old documents. Use tools like WinDirStat or TreeSize to visualize which files are taking up the most space and prioritize their removal.
- Move Files to External Storage: Think about transferring huge files that you don't use often to cloud storage or an external hard disk. By doing this, you may keep your file system better organized in addition to freeing up space on your SSD.
- Cloud Storage: Utilize cloud storage for files that don't need to be stored locally. Many of these services offer a certain amount of free storage, making them a practical solution for freeing up SSD space.
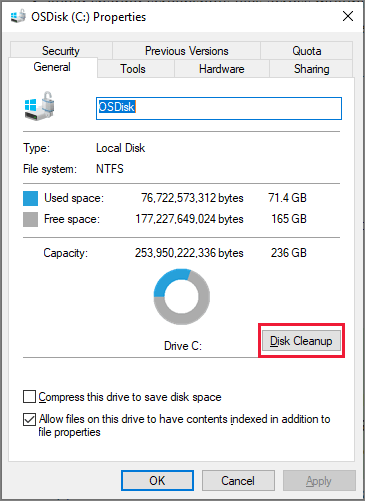
- Disk Cleanup: Running the Disk Cleanup tool on a regular basis can assist in getting rid of system files, temporary files, and other extraneous material that builds up over time. This process helps keep your SSD optimized and free from clutter.
![Disk Cleanup]()
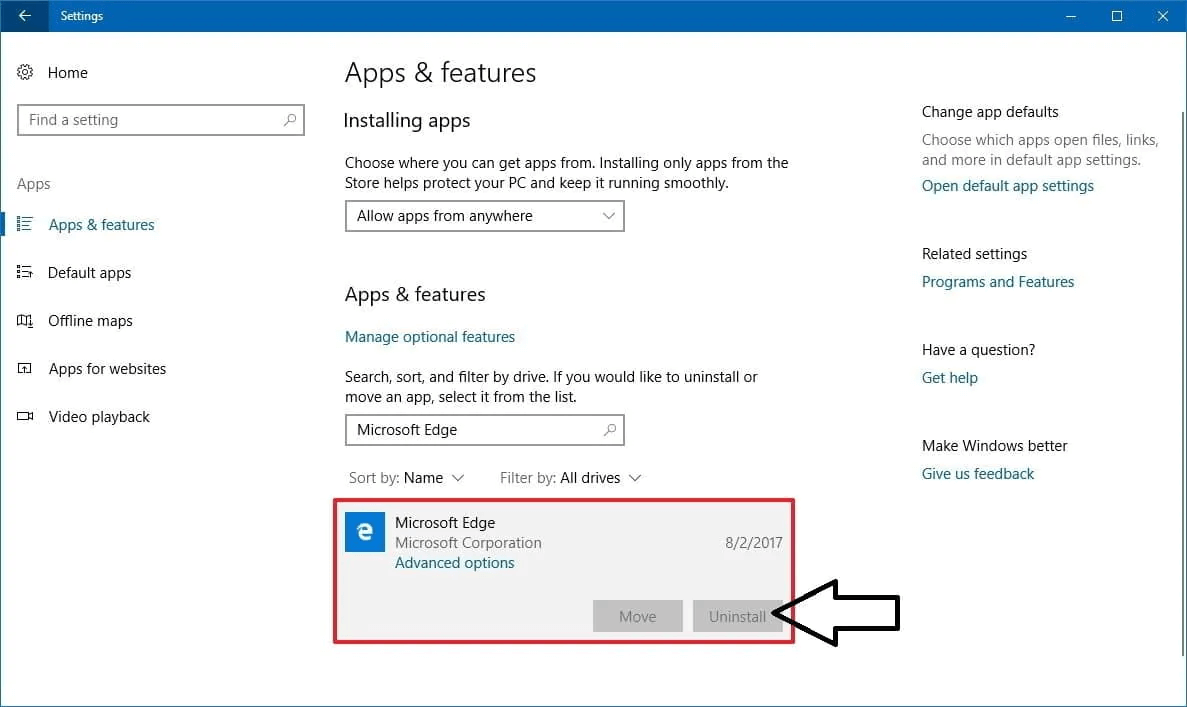
- Uninstall Unused Applications: Applications can take up significant space, especially games and resource-heavy programs. Go through your installed applications and uninstall those you rarely use. On Windows, you can do this by going to Settings > Apps > Apps & features and selecting the application to remove.
![Uninstall Unused Applications]()
● Data Recovery from a Failing SSD
If your SSD is failing and you need to recover data, follow these steps:
- Stop Using the SSD: Continuing to use a failing SSD can cause further damage and data loss. Power down the device immediately.
- Use Data Recovery Software: Try using reputable data recovery software like Donemax Data Recovery, Stellar Data Recovery, or Recuva. Follow the software instructions to recover lost files.
- Professional Recovery Services: Consider getting in touch with a specialized data recovery agency if the software is unable to recover the important data. They can recover data from failed disks thanks to their specialist equipment and knowledge.
For example, you can use data recovery software - Donemax Data Recovery to recover deleted, formatted, erased or lost data from a SSD:
Step 1. Download and install the best SSD data recovery software - Donemax Data Recovery on your computer.
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Recovery, select the SSD to start data recovery.

Step 3. Click on Scan button to deeply scan the SSD and find all recoverable files.
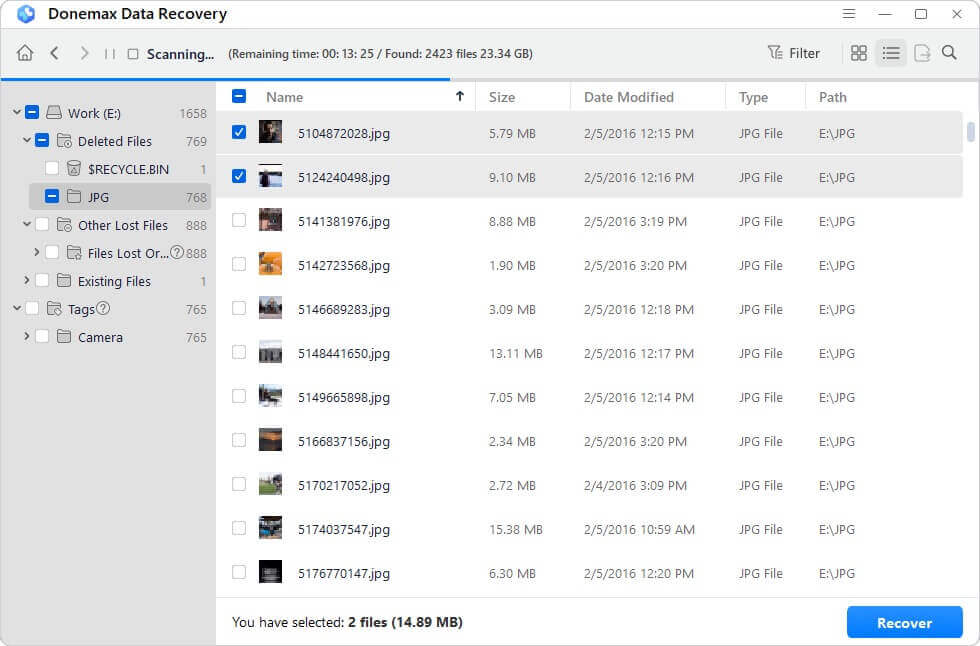
Step 4. Once the scan is completed, you can preview all recoverable files. Then select the wanted files, click on Recover button to save the files.

Preventive Measures for SSD Longevity
● Regular Backups
Always maintain regular backups of your data. Use a combination of cloud storage and external hard drives to ensure that your data is safe in case of SSD failure. Set a schedule for automated backups to simplify the process.
● Keeping Firmware Updated
Regularly check for firmware updates from your SSD manufacturer. Updates can fix bugs, enhance performance, and improve security. Set reminders to check every few months, or subscribe to manufacturer newsletters for notifications.
● Monitoring SSD Health
Make it a habit to monitor your SSD's health regularly. Use the previously mentioned tools to check for warning signs, such as high temperatures or wear levels. Address any issues promptly to prolong the lifespan of your SSD.

How to Protect SSD
Learn how to optimize the SSD and extend the service life of the SSD using simple solutions.
Conclusion
Understanding the reasons behind SSD failures and knowing how to address common issues can save you time, money, and stress. By following the diagnostic steps and fixes outlined in this article, you can troubleshoot problems effectively and maintain the health of your SSD. Remember to perform regular backups, keep your firmware updated, and monitor your drive's health to prevent potential issues in the future. Taking these preventive measures will help you maximize the performance and longevity of your SSD, ensuring your data remains safe and accessible.
Related Articles
- Jan 14, 2025Best 6 Solutions to Fix SSD Is Unreadable
- Feb 05, 20256 Solutions to Fix Can't Format SSD in Disk Management
- Mar 26, 2025MacBook SSD Data Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide
- Feb 24, 2025Reset or Erase SSD with Diskpart (Command Prompt Tool)
- Nov 07, 2024Three Methods to Clone Old SSD to New SSD on Mac
- Nov 07, 2024How to Recover Lost Data from an SSD on Mac?

Christina
Christina is the senior editor of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 4+ years. She mainly writes the guides and solutions about data erasure, data transferring, data recovery and disk cloning to help users get the most out of their Windows and Mac. She likes to travel, enjoy country music and play games in her spare time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems