100% Effective data recovery software to completely recover deleted, formatted and lost files.
The Basic Input Output System is a set of instructions for the central processing unit (CPU) to follow once the computer is powered. This program is usually located in the EPROM and is read by the CPU.
The two most important steps are identifying the accessible input/output devices (keyboard/mouse/disk drives/printers/video cards/etc.) and loading the OS into the main memory.
After startup, the BIOS software handles data flow between the OS and peripherals, so neither the OS nor application programs need to understand the specifics (such as hardware addresses). United Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) replaced BIOS at the beginning of the 21st century because it can manage bigger disks and run at much higher speeds.
Four Primary Jobs of A BIOS
The basic input/output system (BIOS) lets computers do basic tasks as soon as they boot up. A computer's BIOS is primarily responsible for controlling the startup's first phases, ensuring that the operating system is properly loaded into memory.
Understanding the BIOS's role in the functioning of a contemporary computer may be useful in diagnosing and fixing various hardware and software problems.
POST
Once you turn on your computer, the first thing the BIOS does is run the POST. To ensure it can finish the starting process, the BIOS performs hardware checks during the POST. The system will often beep if the POST has finished successfully.
However, if the test does not pass, the system will often make a sequence of beeping noises. The failure reason may be determined by the total number of beeps, their length, and their pattern.
Startup
After the POST is done, the BIOS will use a bootstrap loader to see whether there are any genuine operating systems installed and if so, it will load that OS into memory. Additionally, the drivers for the BIOS are loaded at this time. Basic hardware drivers allow a computer to interact with and manipulate peripherals like a mouse, keyboard, network adapter, or storage device.
Security
Computer security is another area where BIOS may play a role. A boot password may be set in most BIOS software versions, requiring the user to input the password before the system can boot into the BIOS.
Since the BIOS performs almost all the starting processes, this essentially locks off the whole computer's functionality. Resetting a forgotten BIOS password, however, requires access to some of the most sensitive parts of the computer and may take a considerable amount of time.
Hardware
The BIOS program is stored in your computer's Read-Only Memory (ROM) or a flash memory chip. Knowing where the BIOS is stored on the chip is crucial since it's the first piece of software to assume control of the computer once power is applied.
Your computer's microprocessor wouldn't be able to start the booting procedure if the BIOS wasn't consistently positioned in the same spot on the same chip.
BIOS Key Commands
If you want to go into the BIOS, you need to hit and hold the correct key as soon as your computer boots up. The issue is figuring out which button to push, and the answer might change depending on the motherboard and the maker. Try these most often-used combinations:
- F2: To access the BIOS, use the F2 key, which is standard on many laptops, including Toshiba, Samsung, Sony, Acer, Asus, and Dell.
- F1: The F1 key may also be used by Lenovo and Sony.
- F3: The F3 key is used by certain Sony computers.
- F10: F10 is a function key found on certain HP laptops.
- F12: This Dell model may utilize the F12 key.
- Escape: There is an Escape key on several HP devices.
- Delete: On certain MSI, Asus, and Acer laptops; this is a replacement for the F2 key.
- Volume up: To increase the volume, use the actual volume up button on your Surface device (not the keyboard's volume up key).
Windows Startup Menu
If entering the BIOS by pushing a key isn't working for you, or you'd rather use software, Windows provides an alternative approach. Here is the procedure to follow.
In the Windows search box, type "settings," and then choose the Settings app.
Click Update & Security.
Go to the "Recovery" tab.
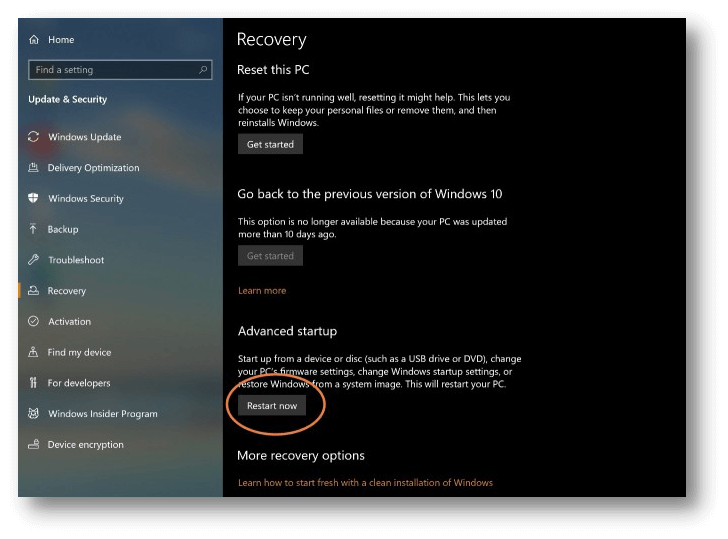
Click the "Restart Now" button in the "Advanced Startup" menu.
Wait for your computer to restart, and then enter the new menu. Click Troubleshoot on the new menu.
Select Advanced Options from the Troubleshoot menu.
After that, choose UEFI Firmware Settings, and then click Restart. After that, the BIOS setup screen should appear.

Conclusion
It's important to remember that each time a user considers modifying the configuration, they should use extreme caution. If the BIOS is misconfigured, the computer may fail to boot.
When updating BIOS, users should exercise caution and ensure that the new BIOS is fully compatible with their current computer setup. If the BIOS is incompatible, the system may get corrupted, preventing the machine from booting.
Related Articles
Donemax Data Recovery

Hot Articles
- How to Install Windows 11 on Unsupported CPU(See What We Do)
- Everything About the EFI System Partition on Windows 11
- Guides on Windows 11 Checker, How to Use it
- What Should I Prepare for the Windows 11 Upgrade
- How to Enable Secure Boot for Windows 11(Complete Guide)
- How to Install Windows 11 from USB
- How to Improve Windows 11 Performance?
- How to Remove Password in Windows 11
- The Difference between Windows 11 and Windows 10| Windows 11 VS Windows 10
- Should You Upgrade to Windows 11? What Benefits of Windows 11?
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.