PAGE CONTENT:
File management is an essential function of any computer operating system. Whether you are storing documents, organizing photos, or managing software files, a file management system helps you navigate and control your data efficiently. Windows users are familiar with File Explorer, the built-in tool for accessing and managing files. However, macOS has its own file management application, called Finder.
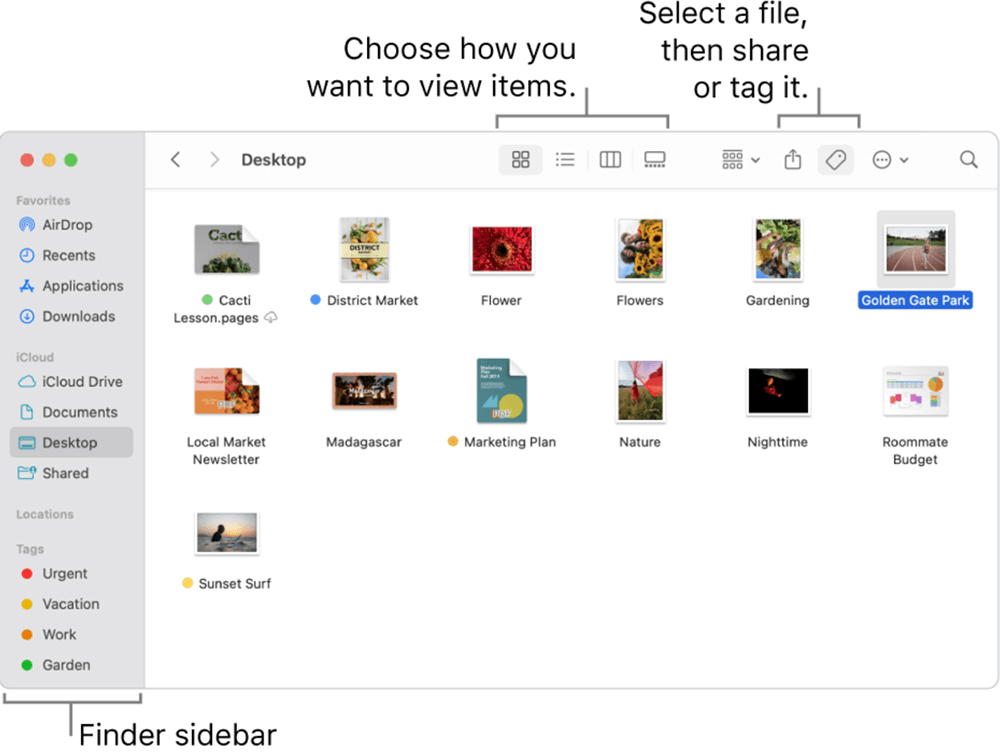
Finder is the default file manager on Mac computers and serves as the main interface for browsing files, applications, and system components. It provides a seamless way to organize data, search for documents, and access external storage devices. In this article, we will explore Finder's functions, features, customization options, and differences from Windows File Explorer, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of macOS's file management system.
What is File Explorer on Mac?
Mac's File Explorer is Finder. Finder is the graphical user interface (GUI) component of macOS, responsible for handling files and applications. It is always running in the background and provides a visual representation of file structures, much like File Explorer in Windows.
Main Functions of Finder:
- Navigating and managing files and folders.
- Opening applications and documents.
- Connecting to external drives and network locations.
- Organizing files using Tags and Smart Folders.
- Providing search functionality via Spotlight.
Finder is always accessible through the smiley face icon in the Dock, and it automatically opens when a Mac boots up. Users can also access Finder through the Command + Space shortcut by searching for it in Spotlight.
Features of Mac's File Explorer - Finder

1. Navigation and File Organization
Finder makes file browsing simple through its Sidebar, which includes shortcuts to frequently used locations such as:
- Favorites: Quick access to commonly used folders like Documents, Downloads, and Desktop.
- iCloud Drive: A cloud storage integration for seamless file access across multiple Apple devices.
- External Drives & Network Locations: USB drives, external hard drives, and connected network servers.
![Navigation and File Organization]()
View Modes: Finder offers multiple ways to view files:
- Icon View: Displays files as large icons with previews.
- List View: Shows detailed file information such as size and date modified.
- Column View: Provides a hierarchical folder structure for quick navigation.
- Gallery View: Useful for previewing images and multimedia files.
2. Searching for Files with Finder and Spotlight
One of Finder's most powerful features is searching. Users can quickly locate files using:
- Finder Search Bar: At the top-right of any Finder window.
![Searching for Files with Finder and Spotlight]()
- Spotlight Search: Accessed via Command + Space, allowing deep file searches across the system.
- Filters & Boolean Operators: Narrow down searches with file types, date modified, or keywords.
3. Organizing Files with Tags and Smart Folders
macOS provides advanced file organization tools:
- Tags: Users can assign color-coded tags to files for quick identification (e.g., "Work," "Personal," or "Important").
- Smart Folders: Dynamic folders that automatically group files based on search criteria (e.g., all PDFs modified in the last week).
4. Quick Look and File Preview
Finder includes Quick Look, which allows users to preview files without opening them. Simply select a file and press Spacebar to view its contents. This feature supports:
- PDFs
- Images
- Videos
- Documents
- Spreadsheets
5. File Actions (Copy, Move, Rename, Delete)
Finder allows users to perform all essential file operations, such as:
- Copying & Moving: Drag and drop files between folders or external drives.
- Renaming Files: Click once on a file name or press Enter to rename it.
- Deleting Files: Move files to the Trash by pressing Command + Delete or dragging them to the Trash bin.
6. External Drives and Network Connections
Finder makes it easy to manage external storage:
- Plugging in a USB flash drive or external hard drive will make it appear in Finder under "Locations."
![External Drives and Network Connections]()
- Network shares from Windows or macOS servers can be accessed via Go > Connect to Server in Finder.
![External Drives and Network Connections]()
- Files can be transferred between Macs using AirDrop, a wireless file-sharing feature.
![External Drives and Network Connections]()
Finder vs. File Explorer: Key Differences
While both Finder on macOS and File Explorer on Windows serve the same fundamental purpose - helping users manage files and navigate their operating system - there are several notable differences between the two. These differences are not just about appearance but also about functionality, usability, and integration with their respective operating systems.
1. Interface and Navigation Differences
The user interface is one of the most noticeable distinctions between Finder and File Explorer.
Finder (macOS)
- Finder features a clean, minimalist design with a Sidebar on the left, a content area in the center, and a top toolbar with essential options.
- It does not have a ribbon-style toolbar like File Explorer, instead relying on a simple set of icons and dropdown menus for actions like renaming, copying, and moving files.
- The Column View in Finder is unique and allows users to navigate deeply nested folders without opening multiple windows. Each column represents a directory level, making it easier to backtrack to parent folders.
- Finder's Gallery View is particularly useful for photographers and designers, providing a large preview of images alongside metadata.
File Explorer (Windows)
- File Explorer uses a ribbon interface at the top, which provides one-click access to frequently used tools like "Copy," "Paste," "Delete," "Rename," and "Sort."
- The Navigation Pane on the left allows quick access to folders, drives, and network locations.
- File Explorer's Details View provides more comprehensive metadata about files, such as resolution for images, artist info for music files, and dimensions for videos.
- Unlike Finder, File Explorer does not have Column View, meaning users may need to open multiple windows or use the back button frequently when navigating deep folders.
Which is More Intuitive?
- Mac users prefer Finder for its simplicity and visual clarity, especially with features like Quick Look and Column View.
- Windows users appreciate File Explorer's detailed file management tools and the customizable ribbon, which reduces the need for right-clicking or searching through menus.
2. File Organization and Tagging
Another major difference between Finder and File Explorer is how they allow users to organize files.
Finder (macOS)
- Finder includes a powerful tagging system that lets users assign color-coded labels to files. These tags help users categorize files more effectively than just using folders.
![File Organization and Tagging on macOS]()
- Files can have multiple tags at once, which means you can tag a file as "Work" and "Urgent", making it appear in both categories when searching.
- Smart Folders dynamically organize files based on rules (e.g., "Show all PDFs created in the last month"), acting as auto-updating virtual folders.
File Explorer (Windows)
- Windows does not have tagging in the same way as Finder, although users can use file properties (metadata) and create custom columns in the Details View.
- Libraries in File Explorer serve a similar purpose to Smart Folders, allowing users to group files from different locations into a single view. However, they are not as flexible as Finder’s tagging system.
- Windows users rely more on folders and directory structures, whereas Finder allows a more flexible approach using tags.
Which is Better for Organization?
- Finder's tagging system provides a more advanced way to categorize and retrieve files quickly, making it great for creative professionals and users who work with large numbers of documents.
- File Explorer's Libraries and Quick Access provide solid organizational tools, but they are not as customizable as Finder's Smart Folders.
3. Search Capabilities: Spotlight vs. Windows Search
One of the most important aspects of file management is searching for files quickly and accurately. Both Finder and File Explorer integrate powerful search tools, but they function differently.
Finder's Search (Spotlight and Finder Search)
- macOS has Spotlight Search (activated via Command + Spacebar), which searches files, applications, emails, calendar events, and even web results.
- Finder itself includes a dedicated search bar that allows users to filter results by type, date modified, file size, and even text inside documents.
- Finder’s search is context-aware, meaning that if you search while inside a folder, it will prioritize results from that folder first.
- Finder can also use Boolean operators (e.g., "invoice AND January") to refine search results.
Windows Search (File Explorer Search Bar and Start Menu Search)
- Windows uses Cortana and Start Menu Search to look for files, applications, settings, and web results.
- The File Explorer search bar allows advanced filtering using properties such as date modified, file type, and size.
- Windows has a feature called Search Indexing, which improves speed but may not always update results instantly when files are moved or renamed.
Which is More Powerful?
- Spotlight Search in macOS is generally faster and more comprehensive, integrating with system-wide searches beyond just files.
- Windows Search is great for finding local files but is sometimes slower if indexing is not optimized.
4. Cloud Integration: iCloud Drive vs. OneDrive
Both macOS and Windows offer cloud integration, allowing users to access files across devices.
Finder's iCloud Drive
- Finder is deeply integrated with iCloud Drive, Apple's cloud storage solution.
- iCloud syncs files across Mac, iPhone, iPad, and even Windows (via the iCloud app).
- It supports Desktop & Documents folder syncing, which means all files in these locations are automatically backed up to iCloud.
File Explorer's OneDrive
- Windows uses OneDrive, Microsoft's cloud storage service.
- OneDrive allows users to store files online and access them across Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android.
- OneDrive's "Files On-Demand" feature lets users see cloud files in File Explorer without downloading them until needed, saving local storage space.
Which is Better?
- iCloud Drive is better for Apple users since it syncs seamlessly across macOS and iOS devices.
- OneDrive is better for Windows users and integrates well with Microsoft 365 (Word, Excel, PowerPoint).
5. File Sharing: AirDrop vs. Nearby Sharing
Finder's AirDrop
- AirDrop allows Mac users to quickly send files to nearby Apple devices via Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
- It is extremely fast and does not require an internet connection.
- Works seamlessly between Mac, iPhone, and iPad.
File Explorer's Nearby Sharing
- Nearby Sharing in Windows allows file transfers between Windows PCs using Bluetooth or Wi-Fi.
- It works similarly to AirDrop but is not as widely used and lacks cross-device support for mobile platforms.
Which is Better?
- AirDrop is faster and more user-friendly, making it a major advantage for Mac users.
- Nearby Sharing is functional but not as polished and lacks integration with smartphones.
Final Verdict: Which is Better?
| Feature | Finder (Mac) | File Explorer (Windows) |
| User Interface | Minimalist, Column View | Ribbon Toolbar, Navigation Pane |
| File Organization | Tags, Smart Folders | Libraries, Quick Access |
| Search | Spotlight, Finder Search | Windows Search, Indexing |
| Cloud Storage | iCloud Drive | OneDrive |
| File Sharing | AirDrop | Nearby Sharing |
Winner?
- If you prefer simplicity and integration across Apple devices, Finder is the superior file manager.
- If you need detailed file metadata, toolbar shortcuts, and deeper customization, File Explorer is better.
Ultimately, both file managers have their strengths, and the best choice depends on your ecosystem and workflow preferences.
Common Finder Issues and How to Fix Them
Although Finder is reliable, users occasionally encounter issues such as:
1. Finder Not Responding
Fix:
- Restart Finder by pressing Command + Option + Esc, selecting Finder, and clicking Relaunch.
![Finder Not Responding]()
- Restart the Mac if the issue persists.
2. Files or Folders Not Showing Up
Fix:
- Check Finder Settings (Finder > Settings > Sidebar) to ensure relevant folders are enabled.
- Restart Finder using the Terminal command:
killall Finder
3. Resetting Finder Preferences
Fix:
If Finder is behaving abnormally, reset its settings by deleting the preferences file:
rm ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.finder.plist && killall Finder
This will restore Finder to its default settings.
Conclusion
Finder is the macOS equivalent of Windows File Explorer, serving as the central hub for file management. It offers a range of features, from file organization and search tools to cloud integration and external drive management. With customization options and powerful navigation tools, Finder helps users efficiently manage their data on a Mac.
By understanding Finder's capabilities and leveraging its shortcuts and features, users can significantly enhance their productivity and file organization experience. Whether you are a longtime Mac user or switching from Windows, mastering Finder is essential for seamless file management on macOS.
Related Articles
- Jul 25, 2024Mac Launchpad: App Manager for Mac
- Dec 06, 2024Learn Everything About Recycle Bin on Windows Computer
- Nov 23, 2024Full Disk Access on Mac: Should I Enable It?
- Sep 24, 2024What Is RAW File System? How to Fix RAW File System?
- Jul 12, 2023What Is NVMe SSD? What Are the Advantages of NVMe SSD?
- Oct 28, 2024What Is Winmail.dat & How to Open It on Mac?

Lucien
Lucien is a writer and a chief programmer of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 5+ years. He has written much of the content on the site and devotes to providing troubleshooting and solution for Windows and Mac users including disk cloning, data recovery, migration, eraser, error fixes.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.






