PAGE CONTENT:
Understanding partition schemes is crucial for anyone managing or configuring a Mac system, whether you're dealing with storage management, system installations, or even setting up dual-boot configurations. Partition schemes define how data is organized on a storage device, and they play a significant role in how operating systems boot, manage, and access data. On Mac systems, there are three primary partition schemes: the GUID Partition Map (GPT), the Master Boot Record (MBR), and the Apple Partition Map (APM). This article aims to explain these partition schemes in detail, highlighting their structure, advantages, and use cases, as well as providing insights on how to manage and choose the right partition scheme for your Mac.
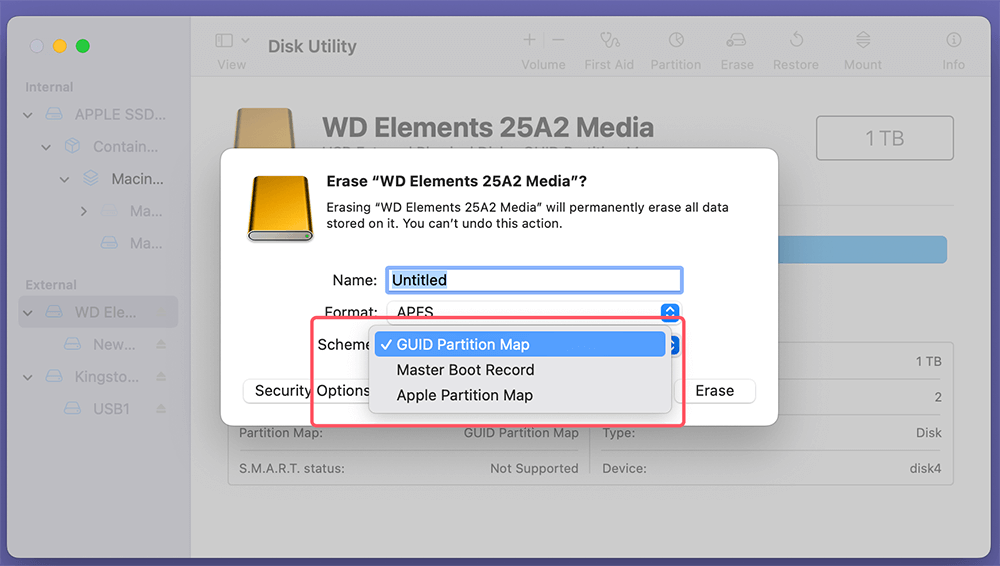
What is Partition Scheme?
A partition scheme refers to the structure used to organize partitions on a disk or storage device. Each partition is essentially a logical division of the disk, which can hold a separate file system and, in most cases, an operating system. The partition scheme defines the way partitions are mapped, the boot loader location, and metadata regarding the disk structure.
In modern computing, the partition scheme used determines the storage device's compatibility with different operating systems. The partition scheme also influences the number of partitions, the disk's size limit, and the system's ability to handle modern storage requirements. Macs, in particular, use distinct partition schemes tailored for different hardware generations and system architectures.
Three Main Partition Schemes on Mac: GPT, MBR, APM
🔖GUID Partition Map (GPT)
1. Overview of GPT
The GUID Partition Map (GPT) is the modern partitioning standard for most new Macs. It replaces the older Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme, which has limitations with regard to the number of partitions and disk sizes. GPT is part of the UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) specification, which is now the standard for most modern operating systems, including macOS.
GPT is designed to work with modern hardware and operating systems, and it has the flexibility to manage large storage devices and support advanced features like partition redundancy and data integrity checks. It has become the default partitioning scheme for Intel-based Macs and is also the standard for Apple Silicon Macs.
2. Structure of GPT
The GPT scheme is characterized by the following features:
- Protective MBR: GPT includes a protective MBR at the beginning of the disk to maintain compatibility with older systems that only understand MBR. This protective MBR prevents older systems from mistakenly writing over GPT disks.
- GPT Header: The GPT header contains metadata about the partition structure, such as the location of the partition table and the size of the disk. It also includes a CRC32 checksum to verify the integrity of the header.
- Partition Table: The partition table holds entries for each partition on the disk. Each entry contains information about the partition type, size, location, and the file system used.
GPT also has a backup partition table located at the end of the disk, providing redundancy in case of corruption.
3. Advantages of GPT
The GPT partition scheme offers several advantages over older schemes like MBR:
- Support for Large Disks: GPT supports disks larger than 2TB, which is a significant limitation in MBR.
- More Partitions: GPT allows for up to 128 partitions on a single disk, compared to MBR's limit of 4 primary partitions.
- Data Integrity: GPT includes a CRC32 checksum for both the header and partition table, ensuring data integrity and providing a safeguard against corruption.
- Flexibility: GPT can store more metadata and is better suited for advanced configurations, including multi-boot setups and disk redundancy.
4. Using GPT on Mac
GPT is the default partition scheme used by macOS, particularly for Intel-based Macs and Apple Silicon Macs. When installing macOS on a new drive, the system will automatically format it with GPT. GPT is compatible with modern file systems like APFS (Apple File System) and HFS+ (Mac OS Extended).
On Mac systems, GPT is used to support both macOS and other operating systems (such as Windows in Boot Camp). When setting up a dual-boot system, GPT is often the preferred choice, as it can handle multiple operating systems more efficiently.
5. Limitations and Compatibility
While GPT offers many advantages, it's not without its limitations. Some older systems, especially those running legacy BIOS, may not support GPT. This can cause compatibility issues, particularly if you need to boot from a GPT-partitioned disk. However, modern Macs, which use UEFI firmware, are fully compatible with GPT.
Additionally, GPT is not universally supported across all operating systems. Although macOS, Windows, and Linux support GPT, older versions of Windows (e.g., Windows XP) and certain Linux distributions may have difficulty recognizing GPT-partitioned disks.
🔖Master Boot Record (MBR)
1. Overview of MBR
The Master Boot Record (MBR) is the older partitioning scheme that was originally developed for DOS-based systems and used on PCs for decades. While it's still in use today for certain systems, it's generally considered obsolete for modern computers, especially those running macOS. MBR has limitations in terms of partition size, the number of partitions, and flexibility compared to GPT.
2. Structure of MBR
MBR works by storing partition information in a special sector at the beginning of the disk, called the "Master Boot Record." This sector contains:
- Boot Loader Code: The first 446 bytes of the MBR are used for boot loader code, which is executed during the boot process to start the operating system.
- Partition Table: The MBR partition table holds entries for up to four primary partitions. Each entry contains information about the partition's size, type, and location.
MBR can only handle four primary partitions, and if more partitions are needed, one primary partition must be converted into an extended partition, which can hold logical partitions.
3. Using MBR on Mac
MBR is not the default partition scheme on modern Macs, but it may still be used for compatibility reasons, particularly on older Mac systems or in dual-boot configurations with Windows. When setting up a dual-boot system using Boot Camp, MBR may be used to format the partition for Windows, especially when working with older or non-UEFI Macs.
4. Advantages and Drawbacks
The primary advantage of MBR is its simplicity and wide compatibility with older systems. However, it has significant drawbacks:
- Limited Partition Size: MBR cannot handle disks larger than 2TB, making it unsuitable for modern large-capacity storage devices.
- Limited Number of Partitions: MBR can only support four primary partitions, which is restrictive if you want to create more partitions on the disk.
- Lack of Redundancy: MBR does not include any data integrity features or redundancy, meaning if the partition table becomes corrupt, it's more difficult to recover data.
5. Conversion between MBR and GPT
Converting an MBR disk to GPT is a relatively simple process on macOS using Disk Utility or the diskutil command in Terminal. However, converting from MBR to GPT requires wiping the disk, which means data loss if it is not backed up. It's important to carefully consider whether conversion is necessary before proceeding.
🔖Apple Partition Map (APM)
1. Overview of APM
The Apple Partition Map (APM) is an older partitioning scheme that was used by PowerPC-based Macs before the transition to Intel-based systems. APM was developed to support the unique needs of the Macintosh architecture, particularly the PowerPC (PPC) processors used in older Macs. APM is not compatible with Intel-based Macs and is largely obsolete, though it may still be found on older Mac systems.
2. Structure of APM
APM uses a partition table to store information about partitions on the disk. This table includes:
- Partition Blocks: These contain information about the size, type, and location of partitions on the disk.
- Directory Blocks: These hold details about the file system used in each partition.
APM is not as flexible or robust as GPT and lacks the data integrity features found in modern partitioning schemes.
3. Using APM on Mac
APM was used by Macs with PowerPC processors, but with the advent of Intel-based Macs and later Apple Silicon, APM has been replaced by GPT. If you’re working with a vintage Mac, you may encounter APM when accessing or modifying the partitions on an old drive.
4. Advantages and Drawbacks
While APM was useful for legacy Macs, it's now largely obsolete. The advantages of APM are limited to legacy compatibility, especially for older PowerPC-based Macs. Its drawbacks include:
- Limited Disk Size Support: APM can't handle disks larger than 2TB.
- Lack of Redundancy: Like MBR, APM lacks built-in redundancy, which makes it more vulnerable to corruption.
- Compatibility Issues: APM cannot be used on Intel-based Macs and is not supported by modern operating systems.
5. Conversion to Other Partition Schemes
If you need to use a disk with an APM partition scheme on a modern Mac, it's often necessary to convert it to GPT. The conversion process typically involves backing up the data and reformatting the drive with GPT.
Also read: how to reformat a disk on Mac.
🔖Comparison of Partition Schemes
When choosing a partition scheme for your Mac, it's important to consider several factors:
- System Compatibility: GPT is the default partition scheme for modern Intel-based Macs and Apple Silicon Macs, while MBR and APM are primarily used for compatibility with older systems.
- Disk Size and Partition Limits: GPT supports disks larger than 2TB and allows up to 128 partitions, making it the best choice for modern storage devices. MBR is limited to 2TB and four primary partitions, while APM is even more restrictive.
- Redundancy and Data Integrity: GPT offers built-in data integrity checks and redundancy, while MBR and APM do not.
How to Choose the Right Partition Scheme for Your Mac?
When deciding on the right partition scheme for your Mac, consider the following factors:
- Disk Size: If you are working with a disk larger than 2TB, GPT is the only viable option.
- Operating System Needs: For dual-booting with Windows, MBR may still be necessary on older Macs, though GPT is typically used for newer systems.
- System Compatibility: Ensure that your Mac's firmware supports the partition scheme you want to use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding partition schemes is essential for managing storage on a Mac system. GPT is the modern standard for macOS, providing flexibility, support for large disks, and data integrity features. MBR and APM, while once commonly used, are now considered legacy formats, with GPT being the preferred choice for modern systems. By selecting the right partition scheme for your system, you ensure optimal performance and compatibility for both macOS and any other operating systems you may wish to use.
Related Articles
- Nov 11, 2024Xcode for Mac Overview: What Is Xcode on Mac and Do You Need It?
- Jul 12, 2023What Is NVMe SSD? What Are the Advantages of NVMe SSD?
- Dec 12, 2024How to Use Dock on Mac and Fix Common Dock Issues?
- Jul 25, 2024Mac Launchpad: App Manager for Mac
- Jun 27, 2023ReFS vs. NTFS: What Are the Differences
- Nov 23, 2024Full Disk Access on Mac: Should I Enable It?

Steven
Steven has been a senior writer & editor of Donemax software since 2020. He's a super nerd and can't imagine the life without a computer. Over 6 years of experience of writing technical solutions and software tesing, he is passionate about providing solutions and tips for Windows and Mac users.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.