Before we start: Mac supports ExFAT and FAT32 fully. You can format and use a drive as ExFAT or FAT32 on Mac. Some issues might cause data loss on ExFAT/FAT32 drive and you can recover data with Donemax Data Recovery for Mac.
PAGE CONTENT:
When working with external drives, memory cards, or flash drives on a Mac, you often come across two popular file systems: ExFAT and FAT32. macOS provides robust support for various file systems. It's essential to understand these two formats. Especially when you need to share data across different operating systems like Windows and Linux.

macOS is famous for supporting a variety of file systems, including its own APFS and HFS+. However, some users need a drive to be compatible with other operating systems. Understanding how macOS interacts with ExFAT and FAT32 is critical. This article will examine can Mac support ExFAT/FAT32 and when they might be the best choice for your needs.
Overview of ExFAT and FAT32 and Can Mac Read-Write ExFAT/FAT32?
ExFAT (Extended File Allocation Table)
ExFAT was developed by Microsoft to address some of the limitations of FAT32. ExFAT is a modern file system to handle larger file sizes and partitions. macOS has native support for ExFAT, meaning you can easily read and write to ExFAT drives. Most modern macOS versions since from macOS 10.6.5 (Snow Leopard) are fully compatible with ExFAT.
Key features of ExFAT:
- Large file size support: ExFAT can support individual files larger than 4GB, unlike FAT32, which has a 4GB file size limit.
- Large partition size support: ExFAT supports partition sizes of up to 128PB, making it suitable for large drives.
- Cross-platform compatible: ExFAT is compatible both Windows and macOS, making it ideal for drives across different platforms.
Use cases for ExFAT on macOS:
- External storage devices: ExFAT is the preferred file system for a large external hard drive, SSD, or USB flash drive.
- SD cards and USB drives: Many SD cards and USB sticks use file system ExFAT.
- Large file storage: ExFAT allows the storage of files larger than 4GB
Advantages of using ExFAT on macOS:
- Cross-platform compatible: ExFAT is fully compatible with both Mac and Windows.
- Handling large files: The file system ExFAT supports files larger than 4GB.
- Efficient file management: ExFAT is a lightweight file system that performs well on large drives.
FAT32 (File Allocation Table 32)
Microsoft introduced the file system FAT32 to be compatible with virtually all operating systems. macOS also supports FAT32 but it is not commonly used on newer devices because of the limitations. Nevertheless, FAT32 is still compatible with macOS, and users can easily read and write to FAT32-formatted drives.
Key features of FAT32:
- Universal compatible: FAT32 is compatible with almost all operating systems, including macOS, Windows, and Linux.
- File size limitation: FAT32 can only store files up to 4GB.
- Partition size limitation: FAT32 supports partitions up to 2TB. However, users often format partitions larger than 32GB to NTFS or ExFAT.
Use cases for FAT32 on macOS:
- Legacy devices: Some old external drives or memory cards, may use FAT32 as their default file system.
- Small file transfers: For small files or when working with devices that have limited storage, FAT32 can still be useful.
Limitations of FAT32 on macOS:
- 4GB file size limit: FAT32 cannot store individual files larger than 4GB.
- Partition size limit: FAT32 can only support partitions up to 2TB in size. Windows systems often cannot recognize or support FAT32 partitions over 32GB.
- Performance limitations: While FAT32 performs well on small drives or older devices. FAT32 lacks the efficiency when managing larger data sets.
How to Format Drives in ExFAT or FAT32 on macOS?
How to use exfat/fat32 drive on mac? First, you need to format the drive to exFAT or FAT32. Formatting a drive in ExFAT/FAT32 on macOS is relatively straightforward using the built-in Disk Utility app. Here's how
Formatting to ExFAT:
- Connect the drive to your Mac and open Disk Utility.
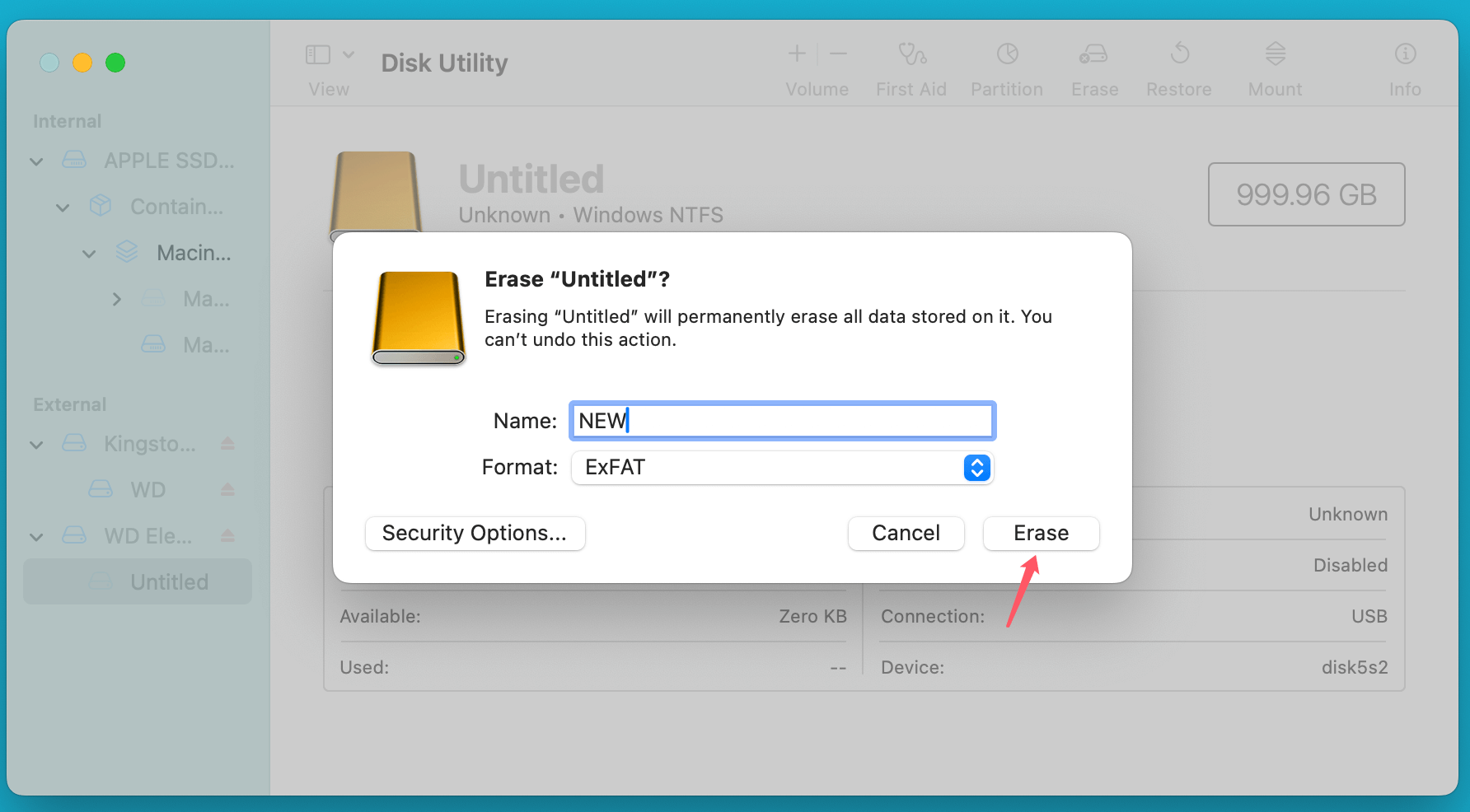
- Select the drive and click on the Erase button.
- Select file system ExFAT as the format. Enter the name for the drive and click Erase.
Formatting to FAT32:
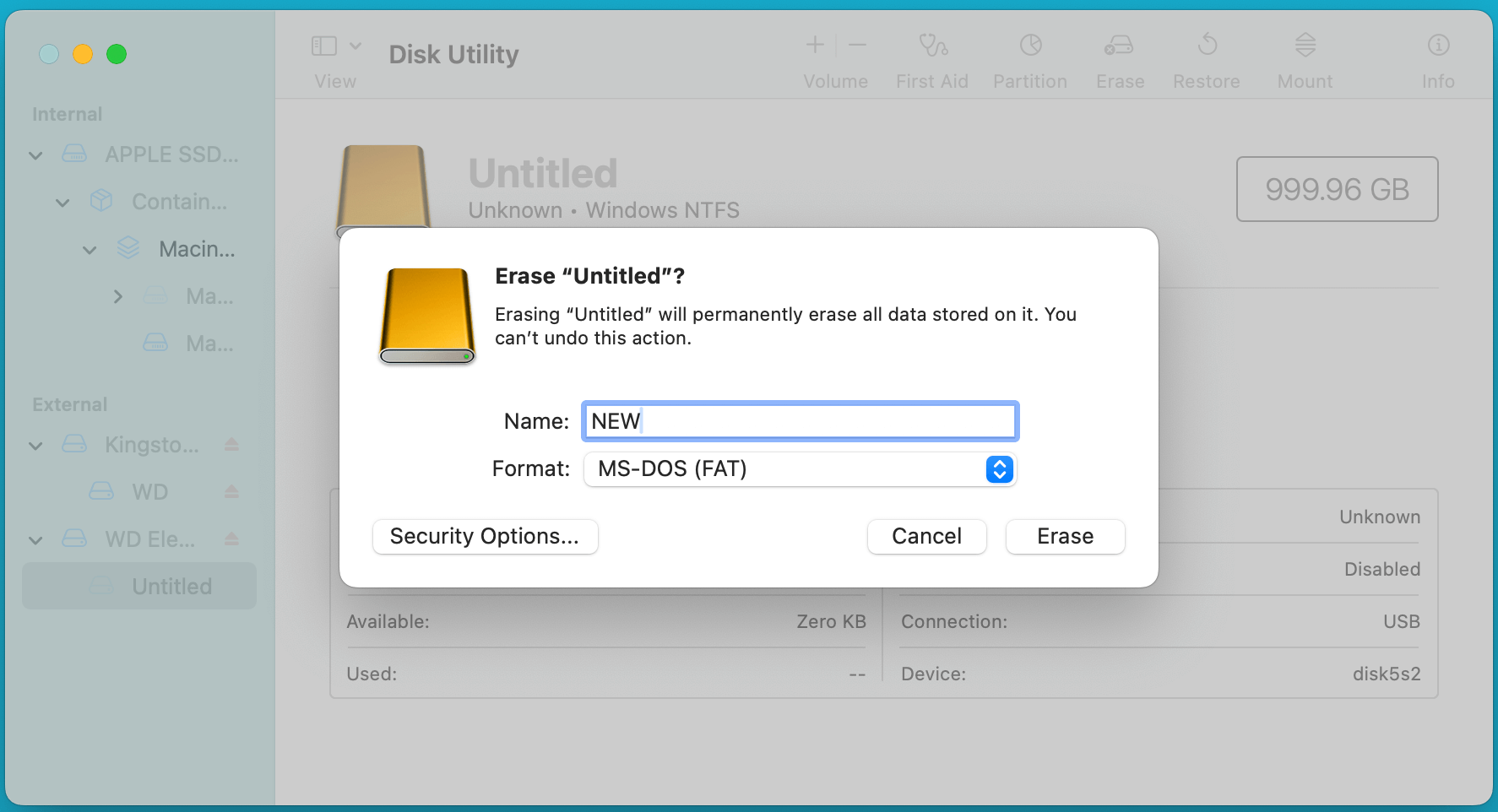
- Follow the same steps to open Disk Utility and select your drive. Click on Erase.
- Select MS-DOS (FAT), which is the macOS representation of FAT32.
- Name the drive and click Erase.
💡 Note: macOS limits FAT32 formatting to drives of 32GB or less. For larger drives, ExFAT is recommended.
Differences Between ExFAT and FAT32 on macOS:
While both ExFAT and FAT32 are compatible with macOS, they differ in several important aspects. Here's a comparison to help you decide which file system to use:
| Feature | ExFAT | FAT32 |
|---|---|---|
| File Size Limit | 16EB (exabyte) | 4GB |
| Partition Size Limit | 128PB (petabyte) | 2TB |
| Cross-Platform Support | Windows, macOS, Linux | Windows, macOS, Linux, Devices |
| Performance | Efficient for large files | Slower on large volumes |
| Use Case | Large files, high-capacity devices | Small files, legacy devices |
Common Issues with ExFAT and FAT32 on macOS:
While both ExFAT and FAT32 are widely supported, users might encounter some issues. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
- ExFAT drive not mounting: If Mac cannot recognize the ExFAT drive, it might be not compatible or there are issues with the drive. Try reconnecting the drive, running Disk Utility to repair it, or reformatting it.
- FAT32 partitions larger than 32GB: macOS limits FAT32 formatting to 32GB partitions. To format a drive larger than that, you must use ExFAT or another file system.
How to Recover Lost Data from FAT32 or ExFAT Drive on Mac?
Some issues may happen on ExFAT or FAT32 drive, like data loss. You may delete or lose files from the ExFAT/FAT32 drive on Mac. You can use Mac data recovery software to get the lost files back.
Step 1. Donemax Data Recovery for Mac is a reliable Mac data recovery application. Just download and install the software on your Mac.
Donemax Data Recovery for Mac
- Effective to recover data from HDD, SSD, USB flash drive, memory card, etc.
- Support data recovery for deleted, formatted or other lost data.
- Easily recover missing pictures, videos, documents, and other files.
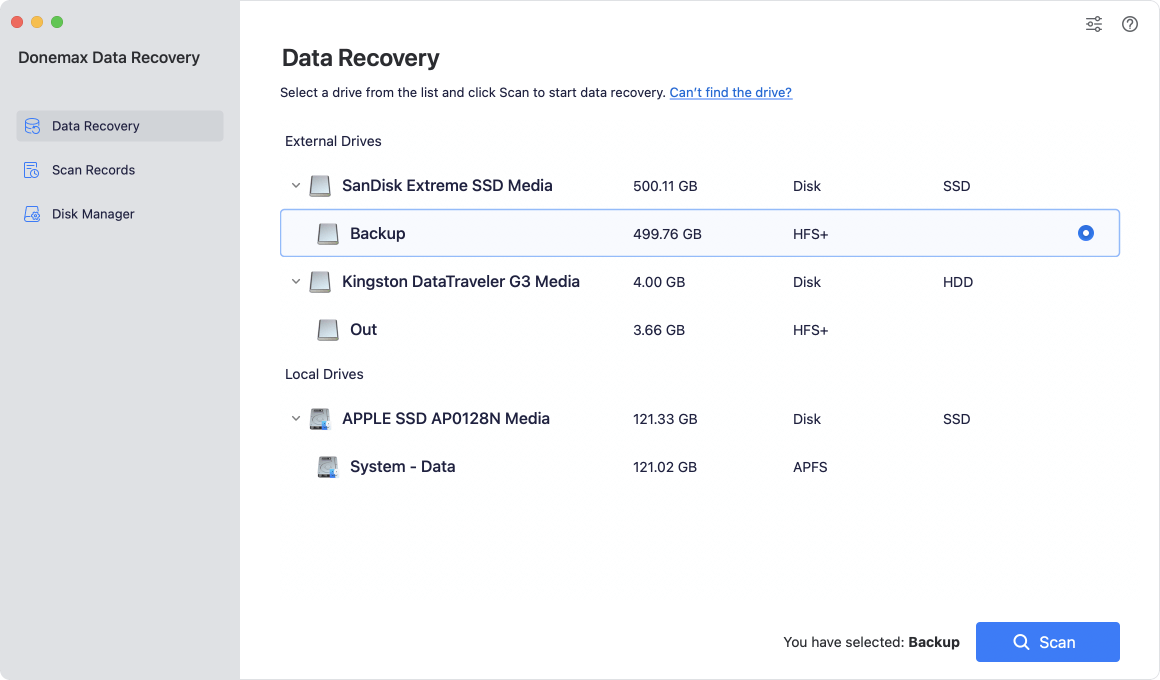
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Recovery for Mac, then select the ExFAT or FAT32 drive to start data recovery.
Step 3. Click on Scan button to deeply scan the selected drive and find all missing files.

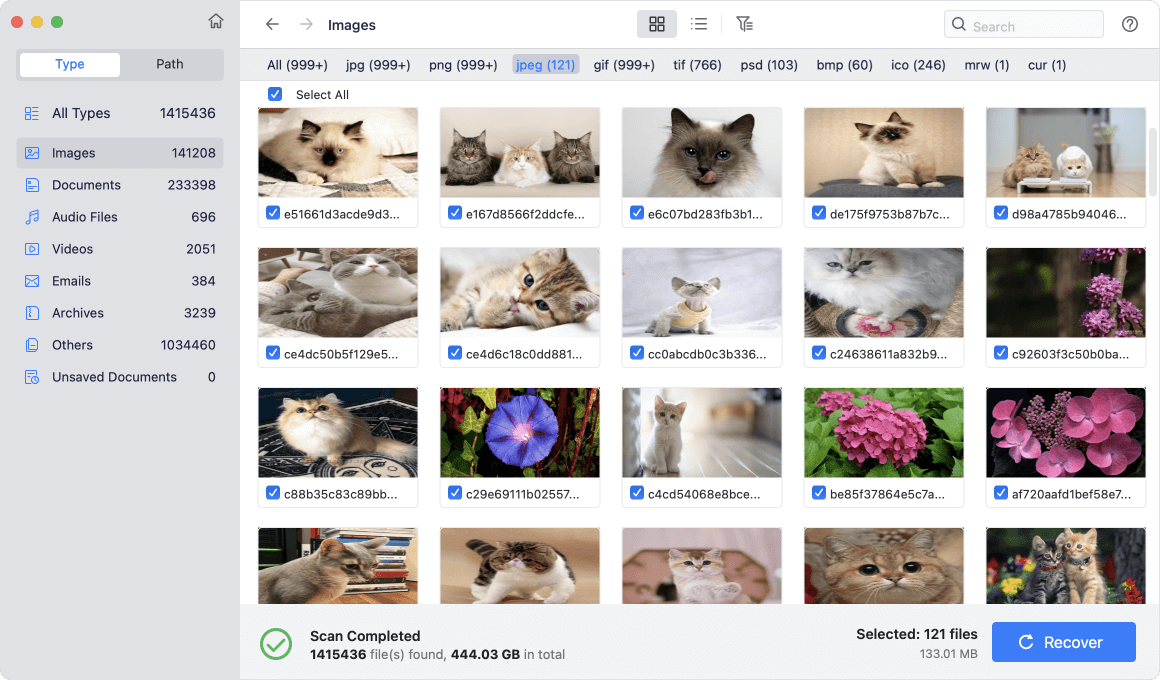
Step 4. After the scan is completed, you can preview all files. You can select the wanted files and click the Recover button to save the files.
Conclusion
macOS fully supports both ExFAT and FAT32, making it easy to work with external drives, USB sticks, and SD cards. While ExFAT is the better choice for modern storage needs because of its support for large files and partitions. FAT32 remains compatible for smaller drives or legacy devices. Understanding the differences of both file systems can help you make the best decision based on your needs.


Donemax Data Recovery for Mac
Donemax Data Recovery for Mac is one of the best Mac data recovery software. It is easy-to-use and can help in recovering deleted, formatted, inaccessible or lost data from Mac HDD/SSD, external disk, USB drive, SD card, camera or other storage devices.
Related Articles
- Dec 18, 2024External Hard Drive Works on Windows, but Not Working on Mac: 7 Solutions to Fix It
- Jan 14, 2025Convert GPM (GUID Partition Map, GPT) Disk to MBR (Master Boot Record) on Mac
- Feb 17, 2024How to Format SK Hynix Beetle X31 SSD for Mac?
- Feb 06, 2024How to Format Lexar Portable SSD for Mac?
- Feb 19, 2024How to Use Samsung Portable SSD T7 on Mac?
- Jul 27, 20257 Methods to Fix External Hard Drive Not Showing Up on macOS Tahoe 26

Christina
Christina is the senior editor of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 4+ years. She mainly writes the guides and solutions about data erasure, data transferring, data recovery and disk cloning to help users get the most out of their Windows and Mac. She likes to travel, enjoy country music and play games in her spare time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems