PAGE CONTENT:
Formatting a drive is a common task that often accompanies the need to store or transfer files between devices. One of the popular formats for external drives is FAT32, a file system that's widely compatible with different operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and even gaming consoles. Understanding how to format a drive to FAT32 can be highly beneficial, whether you're preparing a USB drive for use on multiple devices, setting up a portable hard drive, or simply need to wipe an old drive clean.
This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to format a drive to FAT32, explain when it's necessary, and walk you through the steps on various operating systems. We'll also touch on the advantages and limitations of using FAT32 compared to other file systems.
About FAT32
Before we proceed with the formatting, let's clarify what FAT32 is. File Allocation Table 32-bit is known as FAT32. In order to support bigger file and partition sizes, Microsoft released this older file system in 1996, replacing FAT16. FAT32 is widely regarded as one of the most compatible file systems because it works with virtually any device that supports USB storage, including older devices that might not support newer formats like NTFS or exFAT.

When to Use FAT32:
The primary reason to format a drive to FAT32 is compatibility. FAT32 can be read and written to by most devices, from computers to gaming consoles, smart TVs, and even cameras. Here are some common use cases for FAT32 formatting:
- Cross-platform Compatibility: If you need to transfer files between different operating systems, FAT32 ensures seamless file access across all these platforms.
- Older Devices: Some older hardware, such as media players and game consoles, only recognize FAT32-formatted drives.
- Small Storage Devices: FAT32 works well for smaller USB drives or memory cards that don't require large file storage capacity.
- System Booting: Many bootable drives, such as those used for installing operating systems, need to be formatted to FAT32 to ensure compatibility with BIOS or UEFI.
However, it is significant to note the limitations of FAT32, which include a 4GB maximum file size and a 2TB partition size limit. For larger files or partitions, a format like exFAT or NTFS may be more suitable.
FAT32 vs. ExFAT vs. NTFS
Compare FAT32 to ExFAT and NTFS, find why you should or should not choose FAT32 as the file system of your drive.
How to Format a Drive to FAT32 on Windows?
Windows offers multiple ways to format a drive, either using built-in tools like File Explorer and Disk Management or via the Command Prompt. Here's a step-by-step guide for each method:
1. Using File Explorer
File Explorer is the most user-friendly method for formatting a drive on Windows. It's quick and easy for users who are not as tech-savvy.
Step 1. Insert your USB drive or external hard drive into your computer.
Step 2. Open File Explorer by pressing Windows + E or navigating through the Start menu.
Step 3. In the This PC section, locate your drive.
Step 4. Right-click on the drive and select Format.
Step 5. A window will pop up with several formatting options. Under File System, select FAT32.

Step 6. You can give your drive a name by entering a new label under Volume Label.
Step 7. Ensure that the Quick Format option is checked (this skips the thorough data wipe but is faster).
Step 8. Click Start, and after a few moments, your drive will be formatted to FAT32.
2. Using Disk Management
Disk Management provides more control over the formatting process, and it's also useful for managing partitions.
Step 1. From the menu, choose Disk Management by pressing Windows + X.
Step 2. From the list of accessible drives, choose the disk that has to be formatted.
Step 3. Select Format with a right-click on the drive.

Step 4. Choose FAT32 from the File System selection in the format box.
Step 5. Set the Allocation Unit Size to Default unless you have specific requirements.
Step 6. Click OK, and the system will format your drive.
3. Using Command Prompt
For advanced users or those who prefer working through command lines, the Command Prompt offers another way to format a drive.
Step 1. Enter cmd into the Windows search box to launch the Command Prompt, then choose Run as Administrator.
Step 2. Type the following command to display a list of drives:
list disk
Step 3. Identify your drive from the list and select it by typing:
select disk X
Replace X with the number corresponding to your drive.
Step 4. Now type the command to format the drive:
format fs=fat32 quick
Step 5. Wait for the process to complete, and your drive will be formatted to FAT32.

How to Format a Drive to FAT32 on macOS?
If you're using macOS, you'll need to use Disk Utility, Apple's built-in drive management tool, to format a drive to FAT32. Here's how:
Step 1. Insert your USB drive or external hard drive into your Mac.
Step 2. Open Disk Utility by searching for it in Spotlight (Command + Space) or finding it in Applications > Utilities.
Step 3. From the left-hand column of Disk Utility, choose the drive that has to be formatted.
Step 4. Select the Erase option located at the window's top.

Step 5. In the Erase window, select MS-DOS (FAT) from the Format dropdown menu (this is the macOS label for FAT32).

Step 6. Give the drive a name under the Name field, if desired.
Step 7. Click Erase, and your drive will be formatted to FAT32.
Limitations of FAT32 and Alternatives
FAT32 is one of the most universally supported file systems, but it comes with several limitations that may make it unsuitable for certain tasks. The most notable limitations include:
- 4GB File Size Limit: FAT32 cannot handle files larger than 4GB, which can be problematic if you need to store large video files, disk images, or software installations. For example, a 10-minute 4K video shot in ProRes or other high-definition formats can easily exceed 10GB. In cases where you are working with such files, FAT32 becomes unworkable. This is where alternatives like exFAT or NTFS step in, providing greater scalability and file size flexibility.
- 2TB Partition Limit: FAT32 is limited to a maximum partition size of 2TB, meaning you cannot format larger drives entirely with FAT32. This limitation also creates an issue for backup solutions, especially for businesses. If you need to back up a server or a large set of data onto a single external drive, FAT32 will require splitting the backup across multiple partitions or drives. This not only complicates the process but also introduces the risk of data fragmentation or loss during transfer.
- Fragmentation: FAT32 is prone to fragmentation, which can slow down file access over time as data gets scattered across the drive.
If you need a file system that can handle larger files and partitions, or if you’re working with modern operating systems exclusively, consider using one of these alternatives:
- exFAT: exFAT, or Extended File Allocation Table, is similar to FAT32 but without the 4GB file size or 2TB partition size limits. It's compatible with most modern devices and is a good choice for large external drives.
- NTFS: NTFS (New Technology File System) is the default file system for Windows and is ideal for large drives and files. However, it’s not natively supported by macOS for writing (though it can read NTFS drives).
- APFS: Apple File System (APFS) is optimized for macOS users, offering better performance and reliability, but it's not compatible with Windows or Linux without special software.
How to Unformat FAT32 Drive on Windows and macOS?
Data recovery software can help you recover lost data from a drive which has been formatted to FAT32 (MS-DOS (FAT)). If you have lost data due to formatting a drive to FAT32, you can use data recovery software - such as Donemax Data Recovery to unformat the drive and get all deleted/erased/lost data back!
Step 1. Download and install Donemax Data Recovery on your computer and make sure the formatted drive is connected to the same computer.
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Recovery, select the formatted drive to start data recovery. (HDD/SSD/USB drive/SD card supported.)

Step 3. Click on Scan button to deeply scan the formatted drive and find all recoverable files.
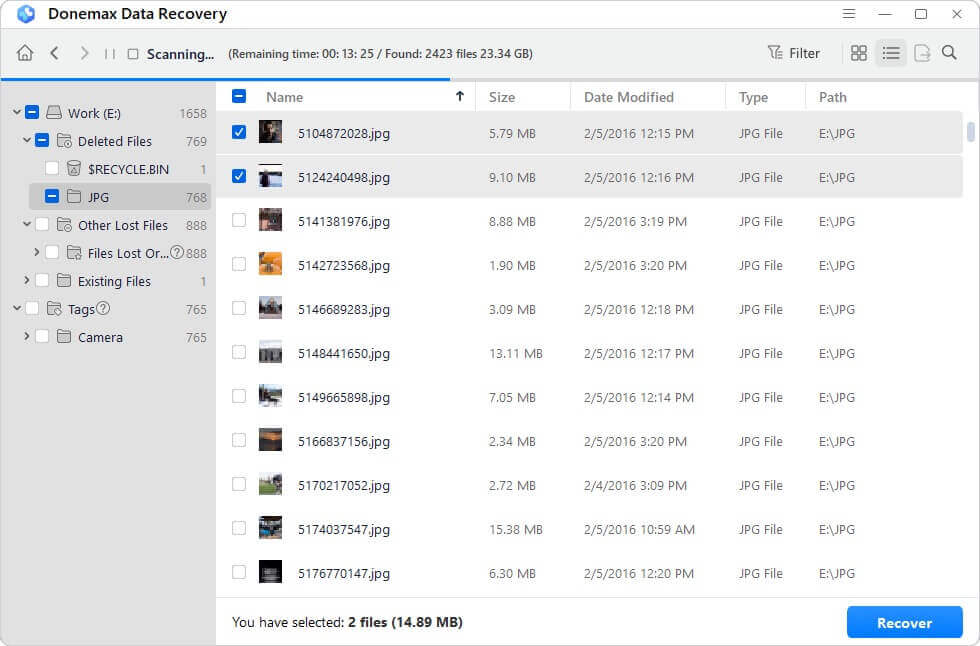
Step 4. Once the scan is completed, you can preview all recoverable files. Then select the wanted files, click on Recover button to save them.

Conclusion
Formatting a drive to FAT32 is a straightforward process on any major operating system, and it offers great cross-platform compatibility for smaller drives and older devices. By following the above step-by-step instructions, you can simply convert your drive to FAT32 and take advantage of smooth file transfers across many systems, regardless of whether you're using Windows, macOS, or Linux.
However, it is beneficial to consider the limitations of FAT32, especially the 4GB file size limit. For larger files or modern use cases, you might want to explore alternatives like exFAT or NTFS, which offer greater flexibility and performance for larger storage devices. Understanding these options allows you to make informed decisions when managing your external drives, ensuring that your storage format aligns with your needs.
FAQs About Format a Drive to FAT32
1. How to format a drive to FAT32 on Windows PC?
It is easy to format a drive to FAT32 on Windows PC.
- Just connect the drive to your computer.
- Open This PC or My Computer, find the drive, right-click the drive.
- Choose Format.
- Select FAT32 as the file system, click Start to format the drive to FAT32.
2. How to format a drive to FAT32 on Mac?
Disk Utility can help you quickly format a drive to FAT32 on Mac:
- Connect the drive to your Mac.
- Open Disk Utility.
- Select the drive, click Erase.
- Select MS-DOS (FAT) as the Format.
- Click Erase again to format the drive to FAT32.
3. How to Format a Drive to FAT32 on Linux?
Linux users can also format drives to FAT32 using built-in tools. Most distributions come with a utility called GParted, which is very similar to Disk Management on Windows.
Step 1. Install GParted if it’s not already available. Open a terminal and type:
sudo apt-get install gparted
Step 2. Once GParted is installed, open it via the terminal or applications menu.
Step 3. Select your drive from the dropdown in the top-right corner.
Step 4. Unmount the drive by right-clicking on its partition and selecting Unmount.
Step 5. Right-click the partition again and choose Format to > fat32.
Step 6. Click the green checkmark to apply changes, and the drive will be formatted to FAT32.
Alternatively, you can use the terminal for formatting by following these steps:
Step 1. Open the terminal and type lsblk to list all drives.
Step 2. Identify the drive you want to format, for example /dev/sdb.
Step 3. Unmount the drive with:
sudo umount /dev/sdb
Step 4. Format the drive using the command:
sudo mkfs.vfat -F 32 /dev/sdb
Step 5. Your drive will now be formatted to FAT32.
4. Is it possible to recover lost data from a formatted drive?
Yes, data recovery software, such as Donemax Data Recovery, can help you recover lost data from a formatted drive.
Related Articles
- Nov 01, 2024CHKDSK is Not Available for RAW Drives: How to Fix It?
- Mar 13, 2025[5 Fixes] Fix Seagate One Touch SSD Not Showing Up on My Computer
- Oct 11, 2024How to Format a Drive to exFAT?
- Dec 23, 20249 Tricks for Fixing the 'CHKDSK Cannot Open Volume for Direct Access' Error
- Feb 21, 2025Can't Format My Memory Card on Windows11/10/8/7? How to Fix It
- Feb 18, 20257 Solutions to Fix Internal Drive Not Showing Up on Windows Without Losing Data

Christina
Christina is the senior editor of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 4+ years. She mainly writes the guides and solutions about data erasure, data transferring, data recovery and disk cloning to help users get the most out of their Windows and Mac. She likes to travel, enjoy country music and play games in her spare time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems