Before we start: Is it possible to recover lost data from an eMMC storage device? Yes, with data recovery program (such as Donemax Data Recovery), you can easily and completely recover lost data from your eMMC storage device.
PAGE CONTENT:
What is eMMC Storage?
eMMC (Embedded MultiMediaCard) is a type of flash storage that is commonly used in mobile devices, tablets, IoT gadgets, automotive systems, and embedded computers. Unlike traditional HDDs or SSDs, eMMC storage is directly soldered onto a device's motherboard, making it a compact and cost-effective storage solution.

Why is eMMC Data Recovery Important?
Data stored on eMMC devices is just as susceptible to loss as on any other storage medium. Whether due to accidental deletion, physical damage, or system corruption, losing data can be a major inconvenience. Unlike SSDs, which often support TRIM functionality for enhanced performance and data management, eMMC storage lacks advanced recovery features, making data retrieval more complex.
This article explores the common causes of eMMC data loss, various recovery methods, available tools, and best practices to prevent data loss in the future.
Common Causes of eMMC Data Loss
1. Physical Damage
Physical damage is one of the primary reasons for eMMC storage failure. Since eMMC chips are soldered directly onto the motherboard, damage to the device can affect data accessibility. Some common causes of physical damage include:
- Water damage: Exposure to moisture can lead to short circuits.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can degrade the solder joints and cause connectivity issues.
- Impact damage: Drops and heavy impacts can break PCB traces or lead to chip dislocation.
2. Logical Corruption
eMMC storage can become unreadable due to software-related issues, including:
- File system corruption: Power failures or improper shutdowns may lead to corrupted file systems.
- Bad sectors: Over time, NAND flash memory degrades, leading to unreadable sections.
- Firmware issues: Firmware corruption can render the eMMC chip inaccessible.
3. Accidental Deletion or Formatting
Users may unintentionally delete important files or format the entire storage, erasing all stored data. If new data is written after accidental deletion, it can overwrite the lost data, making recovery more difficult.
4. Malware and Software Failures
Malicious software can infect the eMMC storage, leading to data loss, corruption, or encryption (as in the case of ransomware attacks). Additionally, failed software updates or system crashes can cause boot issues, making stored data inaccessible.
Methods of eMMC Data Recovery
eMMC data recovery depends on the severity of data loss. There are three main approaches: software-based recovery, hardware-based recovery, and professional services.
Method 1. Recover Lost Data from eMMC with Software
This method is best for logical failures such as accidental deletion, file system corruption, and minor software errors.
1. Steps for Software-Based Recovery
- Stop Using the Device: Avoid writing new data to prevent overwriting lost files.
- Use Data Recovery Software: Specialized recovery software can scan and retrieve lost files.
- Extract Data: Save the recovered files to a different storage medium.
2. Recommended Software for eMMC Recovery
- Donemax Data Recovery
- EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard
- Recuva
- Disk Drill
- R-Studio
3. Limitations of Software Recovery
- Cannot retrieve data from physically damaged eMMC chips.
- May not work if the eMMC chip is not detected by the system.
- Success rate decreases if new data is written after data loss.
Follow the steps below to recover lost data from an eMMC storage device:
Step 1. Download and install Donemax Data Recovery on your computer, then connect the eMMC device to your computer.
Step 2. Open Donemax Data Recovery, select the eMMC to start data recovery.

Step 3. Donemax Data Recovery offers deep scan mode. Just click on Scan button to deeply scan the eMMC device.
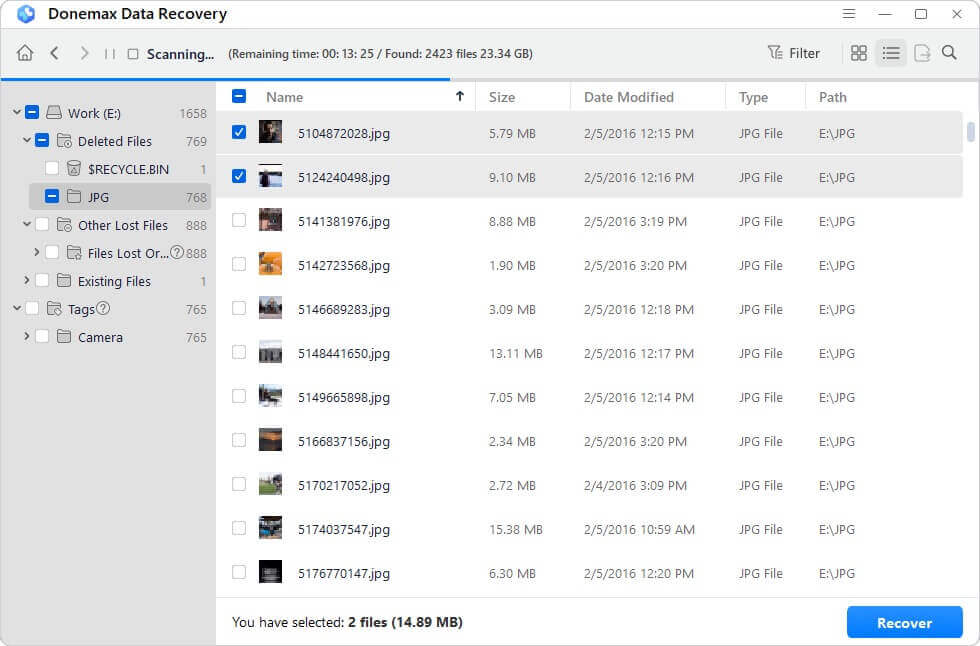
Step 4. Once the scan is completed, you can preview all recoverable files. Then select the wanted files, click on Recover button to save them.

Method 2. Hardware-Based Recovery for eMMC Recovery
This method requires specialized tools, expertise, and sometimes physical modifications to the device.
1. Direct Chip-Off Recovery
Chip-off recovery is one of the most effective methods for extracting data from damaged eMMC storage. It involves physically desoldering the eMMC chip from the motherboard and using specialized equipment to read its contents.
Step-by-Step Chip-Off Recovery Process
Step 1: Identifying the eMMC Chip
Before proceeding with desoldering, it's essential to locate the eMMC chip on the motherboard. Most eMMC chips are labeled with manufacturer markings such as Samsung, Toshiba, SanDisk, Micron, etc. Chip datasheets can help identify pin configurations and storage specifications.
Step 2: Preparing for Chip Removal
- Use a hot air rework station to apply controlled heat to the eMMC chip’s solder joints.
- Protect surrounding components with Kapton tape to avoid damage from heat exposure.
- Use tweezers to carefully lift the chip once the solder has melted.
Step 3: Cleaning the Chip Contacts
- Once removed, clean the chip’s contacts using isopropyl alcohol (IPA) and a fine brush to remove residual solder and flux.
- Inspect under a microscope to ensure clean and intact pads.
Step 4: Reading the eMMC Chip
- Place the cleaned chip into an eMMC reader/programmer such as:
- RT809H Programmer
- Easy JTAG Plus Box
- UFI Box
- Connect the reader to a computer and use software tools to extract raw data.
Step 5: Data Extraction and Reconstruction
- If the chip is detected, create a binary dump (RAW image) of the storage.
- Use forensic tools like R-Studio, WinHex, or Autopsy to analyze and reconstruct file structures.
- Extract and verify recovered data.
Risks and Challenges of Chip-Off Recovery
- Permanent Data Loss: Improper handling can damage the eMMC chip beyond recovery.
- Requires Expertise: Chip-off recovery is complex and should be performed by professionals.
- Expensive Equipment: Requires specialized hardware and software, making it impractical for casual users.
2. JTAG and ISP Recovery
JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) and ISP (In-System Programming) methods offer a non-destructive alternative to chip-off recovery. These methods allow access to eMMC storage without desoldering the chip.
JTAG Recovery Method
JTAG is a hardware interface used for debugging and testing embedded devices. It provides low-level access to the device's memory, making it useful for forensic data extraction.
JTAG Recovery Process:
- Locate the JTAG Pinouts
- JTAG interfaces are often hidden and require schematics to identify test points.
- Some common pin names include TDI (Test Data In), TDO (Test Data Out), TCK (Test Clock), TMS (Test Mode Select).
- Connect JTAG Adapter
- Use a JTAG box (e.g., RIFF Box, Medusa Pro, ATF Box) to establish a connection.
- Solder fine wires or use JTAG clips to attach to test points.
- Access Memory via JTAG Software
- Use software like OpenOCD or IDA Pro to interface with the device.
- Dump raw memory and extract relevant data.
Pros of JTAG Recovery
- No need to remove the eMMC chip.
- Works on locked or inaccessible devices.
- Suitable for forensic investigations.
Cons of JTAG Recovery
- Some devices have disabled JTAG access for security reasons.
- Requires in-depth technical knowledge and tools.
- Slow process compared to direct chip-off recovery.
ISP (In-System Programming) Recovery
ISP is a method that allows direct access to eMMC storage without removing the chip. Instead of using the JTAG interface, ISP connects directly to the eMMC Test Points on the motherboard.
ISP Recovery Process:
- Identify ISP Pinouts:
- ISP pinouts include CLK (Clock), CMD (Command), DAT0 (Data Line), VCC (Power), GND (Ground).
- ISP test points are usually found in manufacturer schematics.
- Use an ISP Adapter or Direct Soldering:
- Option 1: Use an ISP adapter that clips onto the test points.
- Option 2: Manually solder fine wires to the ISP pinouts.
- Connect to an eMMC Reader:
- Use tools like Easy JTAG, UFI Box, or Medusa Pro to communicate with the eMMC chip.
- Bypass system security and access raw memory.
- Extract Data from the eMMC Storage:
- Once the chip is detected, create a raw .bin dump of the storage.
- Analyze and extract lost data using forensic recovery software.
Pros of ISP Recovery:
- Less risk compared to chip-off recovery.
- Works even if the device does not boot.
- Faster than JTAG for direct memory access.
Cons of ISP Recovery:
- Requires detailed motherboard schematics.
- Risk of short-circuiting if improperly soldered.
- Some devices encrypt stored data, making recovery impossible.
Method 3. Professional Data Recovery Services
If DIY recovery attempts fail, professional services may be the best option.
1. When to Seek Professional Help
- If the eMMC chip is physically damaged.
- When the device is completely unresponsive.
- If software and hardware recovery attempts have failed.
2. What to Expect from a Professional Recovery Service
- Diagnosis: The service provider assesses the issue and determines recovery feasibility.
- Recovery Process: Professionals use advanced tools such as cleanrooms and forensic recovery methods.
- Cost: Recovery costs vary from $100 to $1000+, depending on damage severity.
3. Recommended Professional Recovery Services
- DriveSavers
- Gillware Data Recovery
- Ontrack
Prevent Future eMMC Data Loss
To avoid data loss in the future, follow these best practices:
1. Regular Backups
- Use cloud storage (Google Drive, OneDrive, Dropbox).
- Perform local backups on an external HDD/SSD.
2. Proper Handling and Storage
- Avoid exposing devices to moisture and extreme temperatures.
- Use protective cases to prevent physical damage.
3. Use High-Quality eMMC Chips
- Cheap eMMC chips degrade faster.
- Opt for reputable brands (Samsung, Toshiba, SanDisk).
4. Keep Software Updated
- Regular firmware updates prevent system corruption.
- Use antivirus software to protect against malware.
Conclusion
eMMC data recovery can be a complex process depending on the cause of data loss. While software-based recovery can help in minor cases, hardware methods like ISP, JTAG, and chip-off recovery are needed for severe failures. If all else fails, professional data recovery services offer the highest success rate.
To minimize data loss risks, regular backups, proper device handling, and high-quality storage components are essential. By understanding the recovery process and using the right data recovery tools, you can improve your chances of retrieving lost data effectively.


Donemax Data Recovery
One of the best data recovery programs to recover deleted, formatted or lost data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, SD card, camera, RAID, Sever or other storage devices.
Related Articles
- May 19, 20253 Methods to Recover Photos and Videos from Fujifilm Digital Camera
- Jun 28, 2025What is PS File, How to Recover Deleted PS File
- Jun 28, 2025Recover Deleted M2TS File – Complete Guide
- Jul 27, 2025Recover Lost PDF File from a Formatted Drive: Complete Recovery Guide
- May 22, 2025How to Recover Deleted 7-ZIP File (such as .7z file)?
- Jan 17, 2025How to Repair and Recover Corrupted PSD Files?

Maria
Maria is one of the senior writers & editors of Donemax who lives and works in Sydney, Australia. She loves PC, Mac and Internet Technology. She has 6 years of writing articles about data recovery on PC/Mac, disk cloning solution, data eraser and computer OS optimization, etc. She is also interested in testing various software and digital products.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
