100% Effective data recovery software to completely recover deleted, formatted and lost files.
Want to build your personal computer? Knowing how much room you have for storage is essential if that's the case. The use of an SSD compared to a hard disk drive (HHDs) is becoming more common.
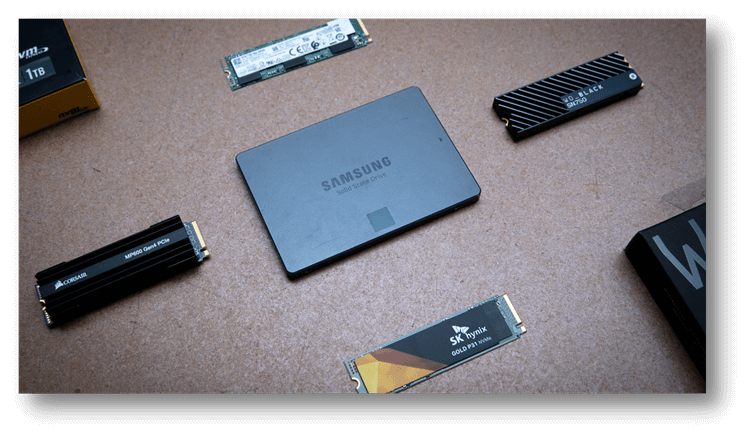
SATA, M.2, PCI Express, and NVM Express are acronyms bandied about carelessly these days. Yet, what exactly distinguishes PCIe, NVMe, M.2, and SATA from one another? Could you permit me to take a peek?
What is SSD-SATA M.2?
SATA M.2 SSDs deliver data at 6Gbps, which is slow relative to newer interfaces (more on that below). SATA-based SSDs are the slowest and utilize hard disk interfaces. SATA SSDs are cheaper. If your PC doesn't have room for a 2.5-inch SSD, SATA M.2 SSDs are a good alternative.
Storage technology has historically relied on SATA connectors. SATA drives require two wires. One powered the PSU while the other transferred data to the motherboard (power supply unit). Computer enclosures with several SATA storage devices were affected by cable congestion. M.2 is used in slim laptops and Ultrabooks because SATA wires don't fit.
M.2 SSDs are still SATA SSDs. Interface and performance distinguish SATA and NVMe M.2 SSDs. SATA M.2 SSDs don't boost speed or performance unless they're NVMe.
NVMe M.2-SSD:
NVMe M.2 SSDs use SSD-specific NVMe protocol. An NVMe SSD with a PCIe bus delivers top performance and speed. PCIe sockets connect NVMe SSDs to the CPU. It permits flash memory to work as an SSD directly over PCIe sockets instead of using the SATA communication driver, which is much slower than NVMe.
NVMe M.2 SSDs perform better than SATA M.2. NVMe M.2 SSDs may theoretically transmit data at 20Gbps, compared to 6Gbps for SATA M.2 SSDs, using the PCIe bus. PCIe supports 1x, 4x, 8x, and 16x lanes. . M.2 form factors with the PCIe bus have x2 and x4 lanes, which limits transfer speeds to 4GB/s.
Does NVMe outperform SATA? Technically. SATA III motherboards can reach 600MB/s, whereas NVMe drives can reach 3,500MB/s. Performance exceeds SATA SSDs regardless of form factor. Only NVMe SSDs exceed SATA SSD transfer speed limitations.

M.2 SSD vs. SATA SSD:
Different Bus Standards: SATA and PCI-E
A computer's central processing unit (CPU), memory, hard drive, and input/output devices are only a few parts connected via a bus. Wires form a transmission harness.
The bus standard specifies the module's orientation, the pins' placement, and other technical details. It allows for processors and devices (including hard disks) to be produced by manufacturers that adhere to the bus standards and requirements.
The SATA Bus Standard is an external hard disk specification. The serial connection mode gives the interface the benefits of a straightforward design, quick data transfers, great efficiency in execution, robust error correction, and hot-plug functionality. The Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus is being phased out in favor of the newer, more efficient PCI Express (PCI-E) Bus standard. It's a high-speed serial point-to-point communication with two channels and a large bandwidth.
Interface type:
When interacting with the rest of a computer, solid-state drives (SSDs) can use either NVMe or SATA. NVMe is indeed faster than SATA, but only slightly.
Yet, M.2 is a specific form factor in and of itself. NVMe and SATA M.2 SSDs are out now; you can choose whichever works best for you.
In some cases, "M.2 SSD" denotes an NVMe drive, whereas "SATA SSD" indicates a 2.5-inch form factor drive. As a result, you shouldn't take such words at face value. Instead, you should peruse the product's technical specifications to estimate the hard drive's speed.
NVMe speed:
NVMe SSDs with PCIe connections have four times faster read and write rates than SATA SSDs.
NVMe enhances parallel Processors, platforms, and applications. NVMe allows concurrent operation with up to 64,000 commands per I/O queue and 64,000 queues. Serial technologies like SCSI have restricted command queues.
Conclusion:
You will likely encounter numerous specialized jargon when searching for a solid-state drive (SSD). But don't let the technical language throw you off. The primary distinction between NVMe and SATA SSDs is the interface, with NVMe employing a PCIe interface and SATA SSDs using a SATA interface, as described above.
The M.2 standard, on the other hand, is a type of solid-state drive (SSD) commonly utilized to bring powerful storage to ultraportable laptops, tablets, and high-end gaming rigs. The M.2 form factor is available for both SATA and PCIe SSDs.
You'll hear both of these terms used together rather frequently. Whether it's an M.2 NVMe SSD or an M.2 SATA SSD, you can be sure that someone will be bragging about their brand-new storage device. Remember that they refer to the physical characteristics and interface of SSDs.
Donemax Data Recovery

Hot Articles
- How to Install Windows 11 on Unsupported CPU(See What We Do)
- Everything About the EFI System Partition on Windows 11
- Guides on Windows 11 Checker, How to Use it
- What Should I Prepare for the Windows 11 Upgrade
- How to Enable Secure Boot for Windows 11(Complete Guide)
- How to Install Windows 11 from USB
- How to Improve Windows 11 Performance?
- How to Remove Password in Windows 11
- The Difference between Windows 11 and Windows 10| Windows 11 VS Windows 10
- Should You Upgrade to Windows 11? What Benefits of Windows 11?
Hot Donemax Products

Clone hard drive with advanced clone technology or create bootable clone for Windows/Mac OS.

Completely and easily recover deleted, formatted, hidden or lost files from hard drive and external storage device.

Certified data erasure software - permanently erase data before selling or donating your disk or any digital device.