Before we start: Donemax Data Eraser is a powerful data erasure programs. It offers certified data erasure standards including U.S. Army AR380-19, DoD 5220.22-M ECE and NIST SP 800-88 to securely and permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, digital camera, SD card, etc. Once the data is erased, it is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method.
PAGE CONTENT:
In an era where data drives decisions, innovation, and connectivity, ensuring its security has never been more critical. Whether stored on hard drives, cloud servers, or personal devices, the lifecycle of data inevitably includes its disposal. Yet, merely deleting a file or formatting a drive is insufficient to ensure the data is irretrievable. This is where data erasure standards come into play, setting protocols for securely eliminating data to protect sensitive information and uphold privacy. This article delves into the significance, methodologies, and evolving landscape of data erasure standards, offering insights into their role in safeguarding digital integrity.
What Are Data Erasure Standards?
Data erasure standards are structured guidelines designed to ensure the secure and complete removal of data from storage devices. Unlike simple deletion, which often leaves recoverable traces, data erasure standards aim to render the data irretrievable, even with advanced forensic techniques. These standards establish protocols for how data should be overwritten, removed, or destroyed, depending on the medium and sensitivity of the information. Central to these guidelines are principles of confidentiality, integrity, and irrecoverability, ensuring that data once erased cannot be reconstructed.
The Need for Data Erasure Standards:
The demand for robust data erasure standards arises from the exponential growth in data generation and the heightened risks of breaches and misuse. Organizations across industries manage sensitive information, from personal identifiers to trade secrets. Without secure erasure, residual data can be exploited, leading to identity theft, corporate espionage, or regulatory violations.
Compliance with legal frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe or the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States further underscores the necessity of adhering to data erasure standards. These regulations mandate organizations to responsibly manage and dispose of data, emphasizing the ethical obligation to protect individuals' privacy. Beyond compliance, adopting rigorous erasure standards builds trust with stakeholders, demonstrating a commitment to security and responsibility.
Overview of Major Data Erasure Standards
Several widely recognized data erasure standards and guidelines have been developed to help organizations securely erase data from storage devices. These standards outline the procedures, methods, and documentation required to ensure that data is irretrievably destroyed.
1. NIST SP 800-88
(National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-88) NIST SP 800-88 is one of the most widely used data erasure standards in the United States. It provides detailed guidance on how to sanitize and dispose of storage media, focusing on three main methods of data sanitization: clear, purge, and destroy. The document also highlights how to handle different types of storage devices, including hard disk drives (HDDs) and SSDs, as well as secure erasure processes for both physical and logical erasure.
- Clear: This method involves overwriting the data on a storage device to make it irretrievable. It is effective for most traditional magnetic storage media.
- Purge: This method is used for more advanced devices like SSDs or devices with embedded controllers that might be resistant to simple overwriting. Purging usually involves the use of specialized tools to securely erase data.
- Destroy: This method physically damages the storage device, making it impossible to recover data. Methods include shredding, crushing, or incineration.
2. DoD 5220.22-M
(Department of Defense Standard) The Department of Defense (DoD) standard, 5220.22-M, was one of the earliest data erasure standards, developed to guide the destruction of classified information. It outlines specific algorithms for overwriting data and specifies the number of times data should be overwritten to ensure it is irretrievable. Although the DoD 5220.22-M standard is still widely referenced, its relevance is gradually decreasing in favor of newer, more comprehensive standards like NIST SP 800-88.
The DoD standard involves multiple overwrites with random data patterns, which provides a level of security suitable for most applications. However, as SSDs and flash-based storage devices became more common, the DoD 5220.22-M method proved less effective, as it does not fully address the unique challenges posed by these devices.
3. ISO/IEC 27001
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard provides a comprehensive framework for information security management systems (ISMS) and is internationally recognized. While it does not focus solely on data erasure, it includes requirements for the secure disposal of data as part of an overall information security strategy. Organizations that implement ISO/IEC 27001 are expected to follow secure data erasure methods to mitigate the risk of data exposure.
The standard provides a risk-based approach, ensuring that data is erased in a manner appropriate to the sensitivity of the information, as well as any regulatory requirements.
4. Other Relevant Standards
- GDPR: The General Data Protection Regulation has specific provisions about data deletion, ensuring that organizations erase personal data when it is no longer necessary.
- HIPAA: The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act includes guidelines on securely erasing healthcare-related data to prevent unauthorized access.
Methods of Data Erasure
Data erasure methods fall into three primary categories: software-based erasure, physical destruction, and hybrid approaches combining both. Each method serves specific needs and scenarios, offering varying degrees of effectiveness and practicality.
- Software-Based Erasure: This method employs specialized programs to overwrite data with random patterns, ensuring its irretrievability. Techniques include single-pass overwrites for efficiency and multi-pass overwrites for greater security. Software-based erasure is suitable for reusable devices, allowing them to return to service without compromising data security.
- Physical Destruction: For data of extreme sensitivity, physically destroying the storage medium ensures its complete elimination. Methods include shredding, incineration, or degaussing (disrupting magnetic fields in devices like hard drives). While effective, physical destruction is resource-intensive and limits device reuse.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining software erasure with physical destruction offers a layered security approach, often used for high-stakes data management in government or defense sectors.
Comparing these methods reveals trade-offs between security, cost, and environmental impact. For instance, while software erasure is cost-effective and eco-friendly, physical destruction guarantees irrecoverability at the expense of sustainability.
Donemax Data Eraser is a reliable software-based data erasure method. It offers certified data erasure standards to help in securely and permanently erasing data from internal drives and external storage devices.
Donemax Data Eraser
- 100% safe and easy-to-use data erasure program for Windows and macOS.
- Permanently erase data from PC/Mac, HDD, SSD and USB drive, SD card, etc.
- Certified data erasure standards including DoD and NIST, etc.
It offers three data erasure modes:
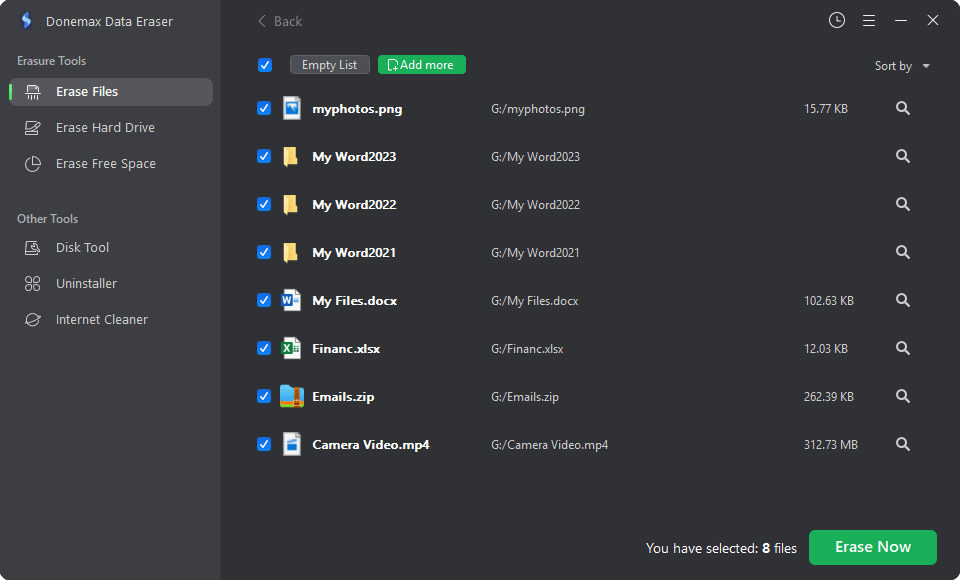
Mode 1. Erase Files - selectively erase files and folders from your local drives or external storage devices. Just add the target files/folders to the erasure list, then click on Erase Now button to permanently erase them.
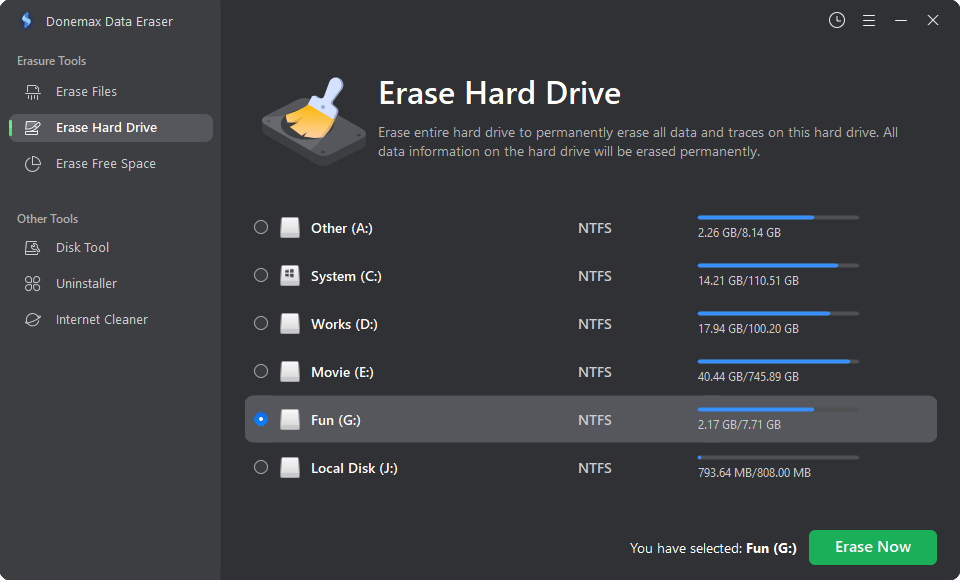
Mode 2. Erase Hard Drive - wipe entire hard drive to permanently erase all data (existing data, deleted/formatted/lost data included) from the drive.
Mode 3. Erase Free Space - wipe free disk space of the drive and permanently erase all deleted/lost data without affecting the existing data.

Compliance and Certification
Adhering to data erasure standards is not merely a best practice but often a legal necessity. Organizations that fail to comply with regulatory requirements risk severe penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Compliance involves implementing standard-aligned practices, documenting processes, and undergoing periodic audits.
Certification programs, such as those offered by the National Association for Information Destruction (NAID), validate an organization's commitment to secure data erasure. These certifications serve as benchmarks of credibility, assuring stakeholders that data is handled responsibly. For professionals, certifications like Certified Data Destruction Specialist (CDDS) enhance expertise and career prospects in an increasingly specialized field.
Audits play a critical role in compliance, providing an independent assessment of an organization’s data sanitization practices. Regular audits ensure adherence to standards, identify gaps, and enable continuous improvement. Together, compliance and certification fortify organizational resilience against data-related risks.
Challenges in Implementing Data Erasure Standards
Despite their importance, implementing data erasure standards poses challenges. Technological complexities arise from the diversity of storage devices, each requiring tailored erasure techniques. Legacy systems, which may lack compatibility with modern erasure methods, further complicate the process.
Operational hurdles include balancing security with cost-effectiveness. High-quality erasure tools and services come at a premium, potentially straining budgets. Additionally, ensuring staff are trained in best practices demands time and resources.
Another challenge lies in managing large-scale data centers or cloud environments, where data is distributed across virtualized infrastructure. Ensuring compliance with erasure standards in such dynamic settings requires robust tools and meticulous oversight.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a proactive approach. Organizations must invest in cutting-edge technologies, foster a culture of security awareness, and engage expert partners to navigate the complexities of data erasure.
Future Trends in Data Erasure Standards
As technology evolves, so too must data erasure standards. Emerging innovations promise to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of data sanitization, shaping the future of the field.
- Blockchain for Erasure Verification: Blockchain's immutable ledger can provide transparent, verifiable records of data erasure activities. This technology has the potential to enhance accountability and traceability, particularly in highly regulated sectors.
- AI-Powered Erasure Tools: Artificial intelligence can optimize data erasure by identifying residual data patterns and adapting erasure methods to specific scenarios. AI-driven tools may reduce human error and streamline complex processes.
- Cloud-Specific Standards: As cloud adoption grows, the need for specialized erasure standards tailored to virtual environments becomes paramount. Future standards may address challenges unique to cloud computing, such as multi-tenancy and geographic data dispersion.
- Sustainability Considerations: The environmental impact of data disposal is gaining attention. Standards may increasingly emphasize eco-friendly practices, encouraging reuse and recycling while maintaining security.
Regulatory landscapes will also continue to evolve, reflecting societal priorities around privacy and security. Staying informed about these changes is essential for organizations to remain compliant and competitive.
Conclusion
Data erasure standards are a cornerstone of modern information security, ensuring that data is not only managed responsibly but also disposed of securely. By adhering to these standards, organizations protect sensitive information, comply with legal mandates, and build trust with stakeholders. The challenges of implementation, while significant, are surmountable with the right strategies and investments.
As technology advances, data erasure standards will continue to adapt, addressing new threats and opportunities. Organizations that prioritize robust erasure practices position themselves as leaders in security and ethics, safeguarding not just their data but their reputations and relationships. In a world increasingly defined by digital connections, the importance of data erasure standards cannot be overstated.


Donemax Data Eraser
One of the best data erasure programs for permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, digital camera and other devices. Once the data is erased, it is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method.
Related Articles
- Jan 09, 2024How to Format External Hard Drive?
- May 17, 20242025 Best USB Drive Data Wipe Software
- Jan 12, 2025How to Securely Wipe Samsung SSD before Disposal? [4 Reliable Methods]
- Jun 28, 2024How to Factory Reset Razer Computer?
- May 06, 2025How to Bypass Recycle Bin When Deleting Files on Windows PC?
- May 10, 2025How to Force Delete a Stubborn File or Folder on Windows Computer? [6 Methods]

Christina
Christina is the senior editor of Donemax software who has worked in the company for 4+ years. She mainly writes the guides and solutions about data erasure, data transferring, data recovery and disk cloning to help users get the most out of their Windows and Mac. She likes to travel, enjoy country music and play games in her spare time.

Gerhard Chou
In order to effectively solve the problems for our customers, every article and troubleshooting solution published on our website has been strictly tested and practiced. Our editors love researching and using computers and testing software, and are willing to help computer users with their problems
